ATM Management System Tutorial: Build with Python & SQLite
Learn How to Create a ATM Management System by Python & SQLite: Step-by-Step Guide for beginner-to-intermediate:
This comprehensive ATM Management System tutorial teaches you how to build a secure, multi-user banking application using Python and SQLite database. Learn professional-grade techniques including SHA-256 PIN hashing for authentication security, transaction audit trails with database persistence, account lockout mechanisms after failed login attempts, and automated receipt generation. This beginner-to-intermediate guide covers defensive programming practices, ACID transaction guarantees, minimum balance enforcement, daily withdrawal limits, and admin panel functionality. Perfect for developers learning database application development, security best practices, and real-world Python CLI project implementation with practical cybersecurity concepts commonly used in banking systems.
Key highlights shown in this project
- Security-first authentication: PIN input is masked and PINs are stored as SHA-256 hashes rather than plaintext.
- Fraud/abuse controls: account lockout after failed attempts, minimum balance rules, daily withdrawal limit enforcement, and ATM cash pool constraints.
- Auditing & traceability: every operation is recorded in a transactions table, and receipts are generated as .txt files for proof and tracking.
Implementation Details
This Python application implements a multi-user ATM system with SQLite-backed persistence, featuring account management, financial transactions, and administrative controls. Key observations:
- Purpose: Provides a complete ATM simulation with login, account creation, deposits, withdrawals, balance inquiry, and administrative oversight.
- Architecture: Monolithic script using SQLite3 for state management; file-based receipt storage; command-line menu interface.
- User Base: Designed for educational demonstration and potential beginner-friendly deployment; includes hardcoded default credentials
- Dependencies: Standard library only (sqlite3, os, re, hashlib, datetime, getpass, typing, contextlib)—no external packages required.
- Critical Risks: Weak admin password hashing strategy (reused salt); potential race conditions in concurrent scenarios; missing input validation in certain withdrawal and deposit paths; hardcoded credentials embedded in source; implicit reliance on writable filesystem for receipts.
- Data Persistence: Three SQLite tables (users, transactions, settings) plus filesystem receipts folder.
- Security Posture: Medium—SHA-256 hashing present, PIN masking via getpass, account lockout mechanism implemented, but salt reuse and SQL parameter passing inconsistencies weaken overall assurance.
System Architecture
ATM System
├── Database Layer (SQLite)
│ ├── Users Table (accounts)
│ ├── Transactions Table (history)
│ └── Settings Table (ATM config)
│
├── Security Layer
│ ├── PIN Hashing (SHA-256)
│ ├── Account Locking (failed attempts)
│ └── Admin Password Protection
│
├── Operations Layer
│ ├── Balance Inquiry
│ ├── Deposit
│ ├── Withdraw (with limits)
│ ├── Mini Statement
│ └── PIN Change
│
├── Admin Layer
│ ├── Account Management
│ ├── ATM Cash Control
│ ├── Transaction Monitoring
│ └── Password Management
│
└── User Interface Layer
├── Main Menu
├── ATM Menu
└── Admin Panel
Complete Source Code
atm_system.py
"""
Single-file Multi-User ATM Management System (Beginner Friendly)
Features:
- Main menu: Login / Create Account / Exit
- Multi-user with JSON file storage (users.json)
- Account number + PIN login (PIN masked via getpass)
- SHA-256 hashed PINs (no plaintext PIN storage)
- Max 3 failed login attempts -> account lock
- Operations after login:
1. Balance Inquiry
2. Deposit
3. Withdraw
4. Mini Statement (last 5)
5. Change PIN
6. Logout
- Transaction history with timestamp
Files created automatically:
- atm_users.json (in same folder as this script)
"""
import sqlite3 # For database operations
import os # For checking file existence
import re # For regular expressions
import hashlib # For SHA-256 PIN hashing (security)
from datetime import datetime, date # For transaction timestamps
from getpass import getpass # For masked PIN input (no echo)
from typing import Dict, Any, Optional, Tuple # Type hints
from contextlib import contextmanager
# -------------------- CONFIG / CONSTANTS --------------------
DB_FILE = "users.db" # SQLite database file
MIN_BALANCE = 500 # Minimum balance required in account
DEFAULT_DAILY_WITHDRAW_LIMIT = 20000.0 # Default daily withdrawal limit per account
DEFAULT_ATM_CASH_POOL = 1000000.0 # Default total cash available in ATM
RECEIPTS_FOLDER = "receipts"
#8f3c5e7d4b2a1f9e6d8c7b5a4e3d2c1b0a9f8e7d6c5b4a3e2d1c0b9a8f7e6d5c
# Name validation rules
MAX_NAME_LENGTH = 50
MIN_NAME_LENGTH = 2
# PIN policies
PIN_LENGTH = 4
DISALLOW_SEQUENTIAL = True
DISALLOW_REPEATING = True
# -------------------- SECURITY UTILITIES --------------------
def hash_password(password: str) -> str:
"""Hash a password using SHA-256"""
salt = "atm_system_secure_salt_2025"
return hashlib.sha256((password + salt).encode()).hexdigest()
ADMIN_PASSWORD = hash_password("SecureAdmin@2025")
def hash_pin(pin: str) -> str:
"""Hashes the PIN using SHA_256 for secure storage."""
return hashlib.sha256(pin.encode()).hexdigest()
def validate_pin_strength(pin: str) -> Tuple[bool, str]:
"""
Validate PIN against security policies.
Returns: (is_valid, error_message)
"""
if len(pin) != PIN_LENGTH:
return False, f"PIN must be {PIN_LENGTH} digits."
if not pin.isdigit():
return False, "PIN must be numeric."
# Check for repeating digits (e.g., 1111, 2222)
if DISALLOW_REPEATING and len(set(pin)) == 1:
return False, "PIN cannot have all repeating digits (e.g., 1111)"
# Check for sequential digits (e.g., 1234, 4321)
if DISALLOW_SEQUENTIAL:
is_ascending = all(int(pin[i]) == int(pin[i-1]) + 1 for i in range(1, len(pin)))
is_descending = all(int(pin[i]) == int(pin[i-1]) - 1 for i in range(1, len(pin)))
if is_ascending or is_descending:
return False, "PIN cannot be sequential (e.g., 1234, 4321)"
return True, ""
def sanitize_name(name: str) -> Tuple[bool, str, str]:
"""
Sanitize and validate user name.
Returns: (is_valid, sanitized_name, error_message)
"""
# Remove extra whitespace
name = " ".join(name.strip().split())
# Check length
if len(name) < MIN_NAME_LENGTH:
return False, "", f"Name must be at least {MIN_NAME_LENGTH} characters."
if len(name) > MAX_NAME_LENGTH:
return False, "", f"Name must be at least {MAX_NAME_LENGTH} characters."
# Check for valid character (letters, spaces, hyphens, apostrophes)
if not re.match(r"^[A-Za-z\s]+$", name):
return False, "", "Name can only contain letters and spaces."
return True, name, ""
def mask_account_number(account_number: str) -> str:
"""Mask account number for receipts (e.g., 1000000000 -> ****000000)"""
if len(account_number) <= 4:
return "****"
return "*" * (len(account_number) - 4) + account_number[-4:]
# -------------------- DB HELPERS --------------------
@contextmanager
# Encapsulate database connection
def get_db_transaction():
conn = sqlite3.connect(DB_FILE) # Open a connection to the SQLite database file
conn.row_factory = sqlite3.Row
cur = conn.cursor()
try:
yield conn, cur
conn.commit()
except Exception as e:
conn.rollback()
raise e
finally:
conn.close()
# Encapsulate database connection
def get_db_connection():
conn = sqlite3.connect(DB_FILE) # Open a connection to the SQLite database file
conn.row_factory = sqlite3.Row
return conn # Return the connection object
def init_db():
conn = get_db_connection() # Opening a connection to the database
cur = conn.cursor() # Creating a cursor object to execute SQL commands
# Users table
cur.execute("""
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS users (
account_number TEXT PRIMARY KEY,
name TEXT NOT NULL,
pin_hash TEXT NOT NULL,
balance REAL NOT NULL,
locked INTEGER NOT NULL DEFAULT 0,
failed_attempts INTEGER NOT NULL DEFAULT 0,
created_at TEXT NOT NULL,
last_withdraw_date TEXT DEFAULT NULL
)
""")
# Transactions table
cur.execute("""
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS transactions (
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT,
account_number TEXT NOT NULL,
type TEXT NOT NULL,
amount REAL NOT NULL,
datetime TEXT NOT NULL,
balance_after REAL NOT NULL,
FOREIGN KEY (account_number) REFERENCES users (account_number)
)
""")
# ATM Settings (for each pool, limits)
cur.execute("""
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS settings (
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT,
atm_cash_pool REAL NOT NULL,
daily_withdraw_limit REAL NOT NULL,
admin_password_hash TEXT NOT NULL
)
""")
# Insert default ATM settings if not exists
cur.execute("SELECT COUNT(*) AS count FROM settings")
if cur.fetchone()["count"] == 0:
cur.execute("INSERT INTO settings (id, atm_cash_pool, daily_withdraw_limit, admin_password_hash) VALUES(1, ?, ?, ?)",
(DEFAULT_ATM_CASH_POOL, DEFAULT_DAILY_WITHDRAW_LIMIT, ADMIN_PASSWORD))
conn.commit() # Commit changes to the database
conn.close() # Close the database connection
# Create Receipts folder
if not os.path.exists(RECEIPTS_FOLDER):
os.makedirs(RECEIPTS_FOLDER)
# -------------------- STORAGE / UTIL FUNCTIONS --------------------
def generate_account_number() -> str:
"""Generate a new 10-digit account number not already in use."""
conn = get_db_connection()
cur = conn.cursor()
base = 1000000000
while True:
acc = str(base)
cur.execute("SELECT 1 FROM users WHERE account_number = ?", (acc,))
if cur.fetchone() is None:
conn.close()
return acc
base += 1
def get_user(account_number: str) -> Optional[Dict[str, Any]]:
"""Retrieve user row as dict or None if not found."""
conn = get_db_connection()
cur = conn.cursor()
cur.execute("SELECT * FROM users WHERE account_number = ?", (account_number,))
row = cur.fetchone() # Retrieves exactly ONE row from the result set of the most recent SQL query executed by the cursor
conn.close()
return dict(row) if row else None
def update_user(user: Dict[str, Any]) -> None:
"""Update user record in DB."""
with get_db_transaction() as (conn, cur):
cur.execute("""
UPDATE users
SET name = ?, pin_hash = ?, balance = ?, locked = ?, failed_attempts = ?, last_withdraw_date = ?
WHERE account_number = ?
""", (
user["name"],
user["pin_hash"],
user["balance"],
int(user.get("locked", False)),
user.get("failed_attempts", 0),
user.get("last_withdraw_date"),
user["account_number"]
))
def create_user_record(account_number: str, name: str, pin_hash: str, initial_deposit: float) -> None:
"""Insert a new user into DB."""
with get_db_transaction() as (conn, cur):
cur.execute("""INSERT INTO users (account_number, name, pin_hash, balance, locked, failed_attempts, created_at, last_withdraw_date)
VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, 0, 0, ?, NULL)""", (account_number, name, pin_hash, initial_deposit, datetime.now().isoformat()))
def verify_pin(user: Dict[str, Any], pin: str) -> bool:
return user["pin_hash"] == hash_pin(pin)
def is_account_locked(user: Dict[str, Any]) -> bool:
"""Check if the account is locked."""
return bool(user.get("locked", 0))
def lock_account(user: Dict[str, Any]) -> None:
"""Lock user account."""
user["locked"] = True
user["failed_attempts"] = 3
update_user(user)
def reset_failed_attempts(user: Dict[str, Any]) -> None:
"""Reset failed login attempts counter."""
user["failed_attempts"] = 0
update_user(user)
def increment_failed_attempts(user: Dict[str, Any]) -> None:
"""Increase failed login attempts and lock after 3."""
user["failed_attempts"] = user.get("failed_attempts", 0) + 1
if user["failed_attempts"] >= 3:
user["locked"] = True
update_user(user)
def record_transaction(account_number: str, tx_type: str, amount: float, balance_after: float) -> None:
"""Record a transaction in the transactions table."""
with get_db_transaction() as (conn, cur):
cur.execute("""
INSERT INTO transactions (account_number, type, amount, datetime, balance_after)
VALUES(?, ?, ?, ?, ?)
""", (account_number, tx_type, amount, datetime.now().isoformat(), balance_after))
return cur.lastrowid
def get_today_withdrawn_amount(account_number: str) -> float:
"""Return total withdraw today for this account."""
user = get_user(account_number)
if not user:
return 0.0
last_withdraw_date = user.get("last_withdraw_date")
today = date.today().isoformat()
# If no withdrawals today, return 0
if last_withdraw_date != today:
return 0.0
conn = get_db_connection()
cur = conn.cursor()
cur.execute("""
SELECT COALESCE(SUM(amount), 0) AS total
FROM transactions
WHERE account_number = ?
AND type = 'WITHDRAW'
AND date(datetime) = date('now', 'localtime')
""", (account_number,))
row = cur.fetchone()
conn.close()
return float(row['total'] if row else 0.0)
def get_settings() -> Dict[str, Any]:
conn = get_db_connection()
cur = conn.cursor()
cur.execute("SELECT * FROM settings WHERE id = 1")
row = cur.fetchone()
conn.close()
if row:
return dict(row)
return {"atm_cash_pool": 0.0, "daily_withdraw_limit": DEFAULT_DAILY_WITHDRAW_LIMIT, "admin_password_hash": ADMIN_PASSWORD}
def update_atm_cash_pool(new_amount: float) -> None:
with get_db_transaction() as (conn, cur):
cur.execute("UPDATE settings SET atm_cash_pool = ? WHERE id = 1", (new_amount,))
# -------------------- RECEIPT GENERATION --------------------------
def generate_receipt(account_number: str, tx_id: int, tx_type: str, amount: float, balance_after: float, additional_info: str = "") -> str:
"""
Generate a receipt file for a transaction
Returns th receipt filename.
"""
user = get_user(account_number)
timestamp = datetime.now()
masked_account = mask_account_number(account_number)
# Create filename
filename = f"receipt_{account_number}_{timestamp.strftime('%d%m%Y_%H%M%S')}_{tx_id}.txt"
filepath = os.path.join(RECEIPTS_FOLDER,filename)
# Generate receipt content
receipt = f"""
{"=" * 50}
ATM TRANSACTION RECEIPT
{"=" * 50}
Date/Time : {timestamp.strftime('%d-%m-%Y %H:%M:%S')}
Transcation ID : {tx_id:08d}
Account : {masked_account}
Name : {user['name'] if user else "Unknown"}
Transaction : {tx_type}
Amount : {amount:.2f}
Balance After : {balance_after:.2f}
{additional_info}
{"=" * 50}
Thank you for using our ATM service!
{"=" * 50}
"""
# Save receipt to file
with open(filepath, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write(receipt)
return filename
# -------------------- AUTHENTICATION FUNCTIONS --------------------
def verify_admin_password() -> bool:
"""Verify admin password against stored hash."""
settings = get_settings()
password = getpass("Enter admin password: ")
# Hash input and compare
input_hash = hash_password(password)
if input_hash != settings['admin_password_hash']:
print('Incorrect admin password.')
return False
return True
def login() -> Tuple[Optional[str], Optional[Dict[str, Any]]]:
print("\n=== Login ===")
acc = input("Enter account number: ").strip()
user = get_user(acc)
if not user:
print("Account not found.")
return None, None
if is_account_locked(user):
print("Account is locked due to multiple failed login attempts.")
return None, None
for _ in range(3):
pin = getpass("Enter 4-digit PIN: ").strip()
if not pin.isdigit() or len(pin) != 4:
print("PIN must be a 4-digit numnber.")
increment_failed_attempts(user)
elif verify_pin(user, pin):
print("Login successful.")
reset_failed_attempts(user)
return acc, get_user(acc) # refresh fresh user data
else:
print("Incorrect PIN.")
increment_failed_attempts(user)
user = get_user(acc) # reload to get update failed attempts/locked status
remaining = 3 - user["failed_attempts"]
if remaining > 0 and not user["locked"]:
print("Atttempts remaining:", remaining)
else:
print('Account locked due to mutiple failed attempts.')
return None, None
return None, None
def create_account() -> None:
"""Register a new user account."""
print("\n=== Create Account ===")
while True:
name = input("Enter your name: ").strip().capitalize()
is_valid, sanitize_named, error = sanitize_name(name)
if not is_valid:
print(f"{error}.")
continue
break
# PIN input and confirmation
while True:
pin = getpass("Set a 4-digit numeric PIN: ")
confirm = getpass("Confirm PIN: ")
if pin != confirm:
print("PINs do not match. Try again.")
continue
is_valid, error = validate_pin_strength(pin)
if not is_valid:
print(f"{error}")
print("PIN Policy:")
print(f" - Must be {PIN_LENGTH} digits.")
print(" - Cannot have repeating digits (e.g., 1111).")
print(" - Cannot have sequential digits (e.g., 1234).")
continue
break
# Initial deposit
while True:
try:
amount = float(input(f"Enter initial deposit (min {MIN_BALANCE}):"))
if amount < MIN_BALANCE:
print(f"Minimum initial deposit is {MIN_BALANCE}.")
continue
break
except ValueError:
print("Invalid amount. Please enter a numeric value.")
# Create user record
pin_hash = hash_pin(pin)
account_number = generate_account_number()
create_user_record(account_number, sanitize_named, pin_hash, amount)
tx_id = record_transaction(account_number, "DEPOSIT", amount, amount)
# Generate receipt
receipt_file = generate_receipt(
account_number, tx_id, "ACCOUNT CREATION - INITIAL DEPOSIT",
amount, amount, "Welcome to out ATM service!"
)
print("\n" + "=" * 50)
print("\nACCOUNT CREATED SUCCESSFULLY!")
print("=" * 50)
print(f"Your account number is: {account_number}")
print(f"Name: {sanitize_named}")
print(f"Initial Balance: {amount:.2f}")
print(f"Receipt saved: {receipt_file}")
print("IMPORTANT: Remember your account number and PIN!")
print("=" * 50)
# -------------------- ATM OPERATIONS --------------------
def balance_inquiry(account_number: str) -> None:
"""Show current balance and record a BALANCE transaction"""
user = get_user(account_number)
if not user:
print("User not found.")
return
print("\n" + "=" * 50)
print("BALANCE INQUIRY")
print("=" * 50)
print(f"\nCurrent balance: {user['balance']:.2f}")
print("=" * 50)
tx_id = record_transaction(account_number, "BALANCE", 0.0, user["balance"])
def deposit(account_number: str) -> None:
"""Deposit money into the account."""
user = get_user(account_number)
if not user:
print("User not found.")
return
print("\n" + "=" * 50)
print(" DEPOSIT")
print("=" * 50)
print(f"\nCurrent balance: {user['balance']:.2f}")
try:
amount = float(input("Enter deposit amount: "))
except ValueError:
print("Invalid amount.")
return
if amount <= 0:
print("Amount must be positive.")
return
try:
with get_db_transaction() as (conn, cur):
# Update balance
new_balance = user['balance'] + amount
cur.execute("""
UPDATE users SET balance = ? WHERE account_number = ?
""", (new_balance, account_number))
# Record transaction
cur.execute("""
INSERT INTO transactions (account_number, type, amount, datetime, balance_after)
VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, ?)
""", (account_number, "DEPOSIT", amount, datetime.now().isoformat(), new_balance))
tx_id = cur.lastrowid
# Generate receipt
receipt_file = generate_receipt(account_number, tx_id, "DEPOSIT", amount, new_balance)
print("\nDeposit successful!")
print(f"New Balance: {new_balance:.2f}")
print(f"Receipt save {receipt_file}")
print("=" * 50)
except Exception as e:
print(f"Transaction failed: {str(e)}")
print("Your balance has not been changed.")
def withdraw(account_number: str) -> None:
"""Withdraw with full transaction rollback protection."""
user = get_user(account_number)
if not user:
print("User not found.")
return
settings = get_settings()
atm_cash = settings["atm_cash_pool"]
daily_limit = settings["daily_withdraw_limit"]
print("\n" + "=" * 70)
print("WITHDRAW")
print("=" * 70)
print(f"\nCurrent balance: {user['balance']:.2f}")
print(f"Minimum balance: {MIN_BALANCE:.2f}")
print(f"Available : {max(0, user['balance'] - MIN_BALANCE):.2f}")
print(f"Daily withdraw limit: {daily_limit:.2f}")
print(f"ATM cash: {atm_cash:.2f}")
try:
amount = float(input("\nEnter withdrawal amount: "))
except ValueError:
print("Invalid amount.")
return
if amount <= 0:
print("Amount must be positive.")
return
# Check min balance rule
if user['balance'] - amount < MIN_BALANCE:
max_withdrawable = max(0.0, user['balance'] - MIN_BALANCE)
print(f"Cannot withdraw. Minimum balance of {MIN_BALANCE:.2f} must remain")
print(f"You can withdraw up to: {max_withdrawable:.2f}")
return
# Check daily limit
today_withdraw = get_today_withdrawn_amount(account_number)
if today_withdraw + amount > daily_limit:
remaining = max(0.0, daily_limit - today_withdraw)
print("\nCannot withdraw this amount due to daily limit.")
print(f"Daily limit: {daily_limit:.2f}")
print(f"Already withdraw today: {today_withdraw:.2f}")
print(f"Reamining today: {remaining:.2f}")
return
if amount > atm_cash:
print("\nATM does not have enough cash.")
print(f"ATM available cash: {atm_cash:.2f}")
return
# Execute withdrawal with transaction protection
try:
with get_db_transaction() as (conn, cur):
new_balance = user['balance'] - amount
today = date.today().isoformat()
cur.execute("""
UPDATE users
SET balance = ?, last_withdraw_date = ?
WHERE account_number = ?
""", (new_balance, today, account_number))
# Update ATM cash pool
new_atm_cash = atm_cash - amount
cur.execute("""
UPDATE settings SET atm_cash_pool = ? WHERE id = 1
""", (new_atm_cash,))
# Record transcation
cur.execute("""
INSERT INTO transactions (account_number, type, amount, datetime, balance_after)
VALUES(?, ?, ?, ?, ?)
""", (account_number, "WITHDRAW", amount, datetime.now().isoformat(), new_balance))
tx_id = cur.lastrowid
# Generate receipt
additional_info = f"ATM Cash After: {new_atm_cash:.2f}\nDaily Withdraw: {today_withdraw + amount:.2f}"
receipt_file = generate_receipt(account_number, tx_id, "WITHDRAW", amount, new_balance, additional_info)
print(f"{amount:.2f} Withdrawn successfully.")
print(f"New balance: {user['balance']:.2f}")
print(f"ATM Cash Remaining: {new_atm_cash:.2f}")
print(f"Receipt saved: {receipt_file}")
print("=" * 70)
except Exception as e:
print(f"Transaction failed and rooled back: {str(e)}")
print("Your balance and ATM cash have not been changed.")
def mini_statement(account_number: str) -> None:
"""Show last 5 transactions."""
conn = get_db_connection()
cur = conn.cursor()
cur.execute("""
SELECT datetime, type, amount, balance_after
FROM transactions
WHERE account_number = ?
ORDER BY id DESC
LIMIT 5
""", (account_number,))
rows = cur.fetchall()
conn.close()
print("\n" + "=" * 70)
print("\nMINI STATEMENT (Last 5 Transactions)")
print("\n" + "=" * 70)
if not rows:
print("No Transactions found.")
return
for tx in rows:
print(f"[{tx['datetime']}] {tx['type']} "
f"Amount: {tx['amount']:.2f} | Balance: {tx['balance_after']:.2f}")
print("\n" + "=" * 70)
def change_pin(account_number: str) -> None:
"""Change the user's PIN."""
user = get_user(account_number)
if not user:
print("User not found.")
return
print("\n" + "=" * 70)
print("CHANGE PIN")
print("\n" + "=" * 70)
old_pin = getpass("Enter current PIN: ")
if not verify_pin(user, old_pin):
print("Incorrect current PIN.")
return
print("\nSet new PIN")
print("PIN policy")
print(f" - Must be {PIN_LENGTH} digits.")
print(f" - Caanot be all same digits (e.g., 1111).")
print(f" - Cannot be sequential (e.g., 1234)")
print()
while True:
new_pin = getpass("Enter new 4-digit PIN: ")
confirm = getpass("Confirm new PIN: ")
if new_pin != confirm:
print("PINs do not match. Try again.")
continue
if new_pin == old_pin:
print("New PIN cannot be the same as the old PIN.")
continue
is_valid, error = validate_pin_strength(new_pin)
if not is_valid:
print(f"{error}")
continue
break
user["pin_hash"] = hash_pin(new_pin)
update_user(user)
tx_id = record_transaction(account_number, "PIN CHANGE", 0.0, user["balance"])
print("PIN Changed successfully.")
print("=" * 70)
# -------------------- ADMIN FUNCTIONS --------------------
def admin_unlock_account():
"""Admin function to unlock a locked account."""
print("\n" + "=" * 70)
print(" ADMIN UNLOCK ACCOUNT")
print("=" * 70)
if not verify_admin_password():
return
# Show all locked account
conn = get_db_connection()
cur = conn.cursor()
cur.execute("""
SELECT account_number, name, failed_attempts
FROM users
WHERE locked = 1
ORDER BY account_number
""")
locked_accounts = cur.fetchall()
conn.close()
if not locked_accounts:
print("\nNo locked accounts found.")
return
print("Locked Accounts")
print("-" * 70)
for acc in locked_accounts:
print(f" Account: {acc['account_number']}")
print(f" Name: {acc['name']}")
print(f" Failed Attempts: {acc['failed_attempts']}")
print()
account_number = input("Enter account number to unlock (or 'all' for all): ").strip()
if account_number.lower() == "all":
with get_db_transaction() as (conn, cur):
cur.execute("""
UPDATE users
SET locked = 0, failed_attempts = 0
WHERE locked = 1
""")
rows_affected = cur.rowcount
print(f"Unlock {rows_affected} accounts(s)")
else:
# Unlock specific account
user = get_user(account_number)
if not user:
print("Account not found.")
return
if not user["locked"]:
print("Account is not locked.")
return
user["locked"] = False
user["failed_attempts"] = 0
update_user(user)
# Log admin action
record_transaction(account_number, "ADMIN_UNLOCK", 0.0, user['balance'])
print(f"\nAccount {account_number} ({user['name']}) has been unlocked.")
print(" User can now login again.")
print("=" * 70)
def admin_view_all_accounts():
"""Admin function to view all accounts."""
print("\n" + "=" * 70)
print(" ADMIN: VIEW ALL ACCOUNTS")
print("=" * 70)
if not verify_admin_password():
return
conn = get_db_connection()
cur = conn.cursor()
cur.execute("""
SELECT account_number, name, balance, locked, failed_attempts
FROM users
ORDER BY account_number
""")
accounts = cur.fetchall()
conn.close()
if not accounts:
print("\nNo accounts found.")
return
print(f"\n{'Acount':<15} {'Name':<20} {'Balance':<12} {'Status':<10} {'Failed':<8}")
print("-" * 70)
for acc in accounts:
locked_status = "LOCKED" if acc['locked'] else "ACTIVE"
print(f"{acc['account_number']:<15} {acc['name']:<20} ₹{acc['balance']:<10.2f} {locked_status:<10} {acc['failed_attempts']:<10}")
print("-" * 70)
print(f"Total Accounts: {len(accounts)}")
print("=" * 70)
def admin_view_atm_cash():
"""View current ATM cash pool."""
print("\n" + "=" * 70)
print(" ADMIN: ATM CASH POOL")
print("=" * 70)
if not verify_admin_password():
return
settings = get_settings()
print(f"\nCurrent ATM Cash Pool: {settings['atm_cash_pool']:.2f}")
print(f"Daily Withdraw Limit: {settings['daily_withdraw_limit']:.2f}")
print("=" * 70)
def admin_refill_atm():
"""Admin function to refill ATM cash pool."""
print("\n" + "=" * 70)
print(" ADMIN: REFILL ATM CASH")
print("=" * 70)
if not verify_admin_password():
return
settings = get_settings()
print(f"\nCurrent ATM Cash Pool: {settings['atm_cash_pool']:.2f}")
try:
amount = float(input("Enter amount to add: "))
except ValueError:
print("Invalid amount.")
return
if amount <= 0:
print("Amount must be positive.")
return
new_pool = settings['atm_cash_pool'] + amount
update_atm_cash_pool(new_pool)
print(f" ATM cash pool updated!")
print(f" Previous: {settings['atm_cash_pool']:.2f}")
print(f" Added: {amount:.2f}")
print(f" New Total: {new_pool:.2f}")
print("=" * 70)
def admin_change_password():
"""Change admin password."""
print("\n" + "=" * 70)
print(" ADMIN: CHANGE PASSWORD")
print("=" * 70)
if not verify_admin_password():
return
print("\nSet new admin password")
print("Requirments:")
print(" - Minimum 8 characters.")
print(" - Mix of letters, numbers, and symbols recommended.")
print()
while True:
new_password = getpass("Enter new admin password: ")
if len(new_password) < 8:
print("Password must be least 8 characters.")
continue
confirm = getpass("Confirm new password: ")
if new_password != confirm:
print("Passwords do not match. Try again.")
continue
break
new_hash = hash_password(new_password)
with get_db_transaction() as (conn, cur):
cur.execute("UPDATE settings SET admin_password_hash = ? WHERE id = 1", (new_hash,))
print("\nAdmin password changed successfully!")
print("Please remember your new password!")
print("=" * 70)
def admin_view_transaction():
"""View recent transactions across all accounts."""
print("\n" + "=" * 70)
print(" ADMIN: RECENT TRANSACTIONS")
print("=" * 70)
if not verify_admin_password():
return
try:
limit = int(input("\n How many recent transactions to show? (default 10): "))
except ValueError:
limit = 10
conn = get_db_connection()
cur = conn.cursor()
cur.execute("""
SELECT t.datetime, t.account_number, u.name, t.type, t.amount, t.balance_after
FROM transactions t
JOIN users u ON t.account_number = u.account_number
ORDER by t.id DESC
LIMIT ?
""", (limit, ))
transactions = cur.fetchall()
conn.close()
if not transactions:
print("\nNo transactions found.")
return
print(f"\n{'Date/Time':<20} {'Account':<12} {'Name':<15} {'Type':<12} {'Amount':<10} {'Balance':<10}")
print("-" * 90)
for tx in transactions:
dt = tx['datetime'][:19]
print(f"{dt:<20} {tx['account_number']:<12} {tx['name']:<15} {tx['type']:<12} ₹{tx['amount']:<8.2f} ₹{tx['balance_after']:<8.2f}")
print("-" * 90)
print("=" * 70)
# -------------------- MENUS --------------------
def atm_menu(account_number: str) -> None:
"""Display ATM operatins menu for logged-in user."""
user = get_user(account_number)
if not user:
print("user not found")
return
while True:
print("\n" + "=" * 70)
print(f" ATM MENU ({user['name']})")
print(f" Welcome {user['name']},")
print(f" Account Number: {account_number}")
print(" 1. Balance Inquiry")
print(" 2. Deposit")
print(" 3. Withdraw")
print(" 4. Mini Statement")
print(" 5. Change PIN")
print(" 6. Logout")
print("=" * 70)
choice = input("Enter your choice (1-6): ").strip()
if choice == "1":
balance_inquiry(account_number)
elif choice == "2":
deposit(account_number)
elif choice == "3":
withdraw(account_number)
elif choice == "4":
mini_statement(account_number)
elif choice == "5":
change_pin(account_number)
elif choice == "6":
print("Logging out...")
break
else:
print("Invalid choice. Please try again.")
input("\nPress Enter to continue...")
def admin_menu():
"""Admin submenu for management tasks."""
while True:
print("\n" + "=" * 70)
print(" ADMIN PANEL")
print("=" * 70)
print(" 1. Unlock Account")
print(" 2. View All Accounts")
print(" 3. View ATM Cash Pool")
print(" 4. Refill ATM cash")
print(" 5. View Recent Transactions")
print(" 6. Change Admin Password")
print(" 7. Back to Main menu")
print("=" * 70)
choice = input("Enter choice (1-6): ").strip()
if choice == "1":
admin_unlock_account()
elif choice == "2":
admin_view_all_accounts()
elif choice == "3":
admin_view_atm_cash()
elif choice == "4":
admin_refill_atm()
elif choice == "5":
admin_view_transaction()
elif choice == "6":
admin_change_password()
elif choice == "7":
print("\nReturning to main menu...")
break
else:
print("Invalid choice")
input("\nPress Enter to continue...")
def main_menu() -> None:
"""Main menu: login, create account, exit"""
while True:
print("\n" + "=" * 70)
print(" MAIN MENU")
print("=" * 70)
print(" 1. Login")
print(" 2. Create Account")
print(" 3. Admin Panel")
print(" 4. Exit")
print("=" * 70)
choice = input("Enter your choice (1-3): ").strip()
if choice == "1":
acc, user = login()
if acc and user:
atm_menu(acc)
elif choice == "2":
create_account()
elif choice == "3":
admin_menu()
elif choice == "4":
print("\n" + "=" * 70)
print(" Thank you for using Python system. Goodbye!")
print("=" * 70)
break
else:
print("Invalid choice. Please try again.")
# -------------------- ENTRY POINT --------------------
if __name__ == "__main__":
print("\n" + "=" * 70)
print(" Initializing ATM System...")
print("=" * 70)
init_db() # Initialize database and tables
print(" Database initialized successfully.")
print("Receipts folder created!")
print("Default Admin Password; SecureAdmin@2025")
print("Change it immediately via Admin Panel!")
print("=" * 70)
main_menu()
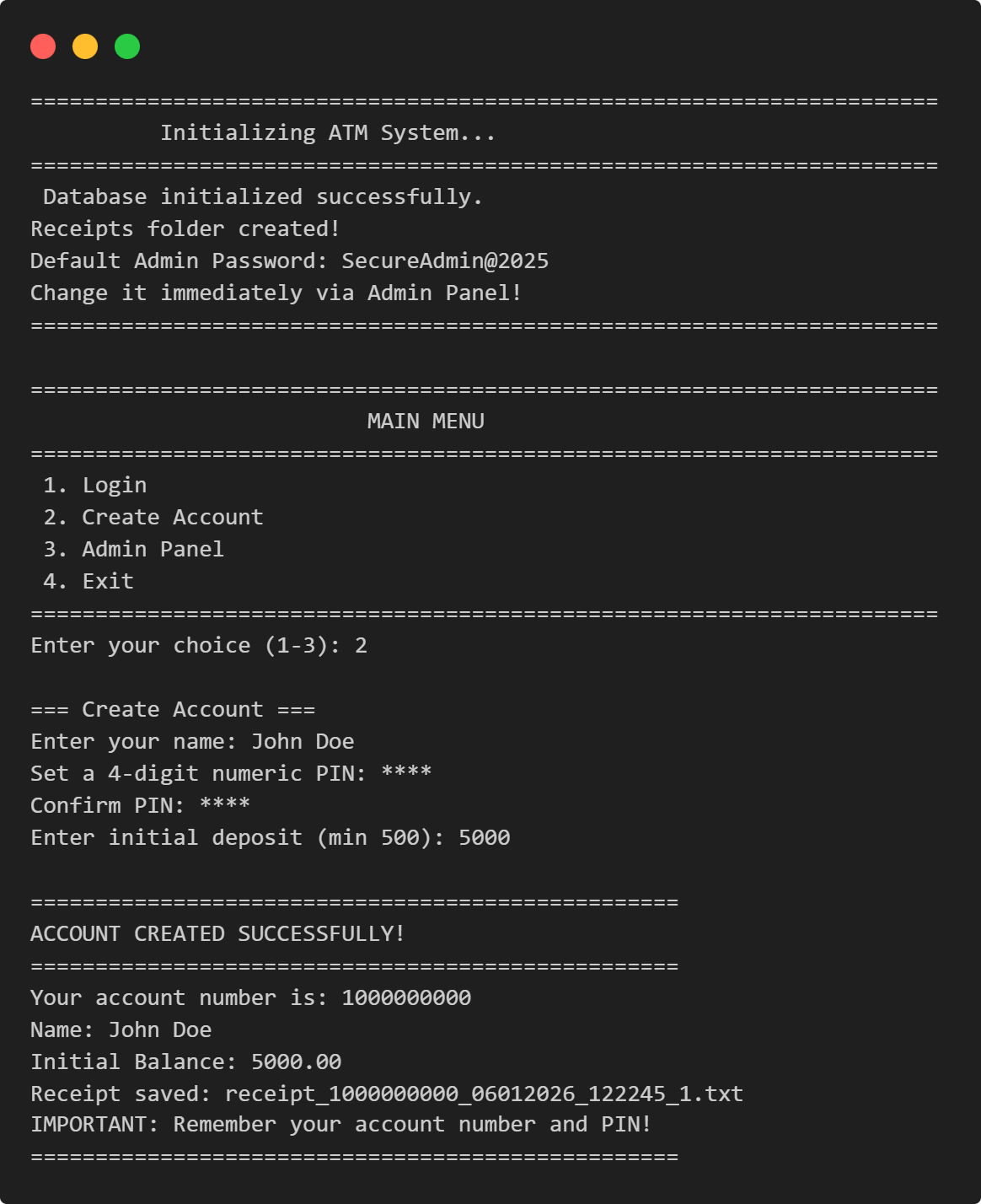
======================================================================
Initializing ATM System...
======================================================================
Database initialized successfully.
Receipts folder created!
Default Admin Password: SecureAdmin@2025
Change it immediately via Admin Panel!
======================================================================
======================================================================
MAIN MENU
======================================================================
1. Login
2. Create Account
3. Admin Panel
4. Exit
======================================================================
Enter your choice (1-3): 2
=== Create Account ===
Enter your name: John Doe
Set a 4-digit numeric PIN: ****
Confirm PIN: ****
Enter initial deposit (min 500): 5000
==================================================
ACCOUNT CREATED SUCCESSFULLY!
==================================================
Your account number is: 1000000000
Name: John Doe
Initial Balance: 5000.00
Receipt saved: receipt_1000000000_06012026_122245_1.txt
IMPORTANT: Remember your account number and PIN!
==================================================
Structure Map
| Section | Purpose | Key Symbols |
|---|---|---|
| Module Docstring | Feature summary and high-level overview | N/A |
| Imports | Bring in standard library utilities | sqlite3, os, re, hashlib, datetime, getpass, typing, contextlib
|
| Global Constants | Configuration knobs (DB file, limits, PIN policy) | DB_FILE, MIN_BALANCE, DEFAULT_DAILY_WITHDRAW_LIMIT, DEFAULT_ATM_CASH_POOL, PIN_LENGTH, DISALLOW_SEQUENTIAL, DISALLOW_REPEATING
|
| Security Utilities | Hashing, PIN/name validation, account number masking | hash_password(), hash_pin(), validate_pin_strength(), sanitize_name(), mask_account_number(), ADMIN_PASSWORD
|
| DB Helpers (Context Managers) | Transaction context manager, connection factory, schema init | get_db_transaction(), get_db_connection(), init_db()
|
| Storage/Util Functions | User CRUD, transaction logging, settings management | generate_account_number(), get_user(), update_user(), create_user_record(), verify_pin(), is_account_locked(), lock_account(), increment_failed_attempts(), record_transaction(), get_today_withdrawn_amount(), get_settings(), update_atm_cash_pool()
|
| Receipt Generation | Write transaction receipt to disk | generate_receipt() |
| Authentication | Admin password verification, user login flow | verify_admin_password(), login() |
| Account Creation | Interactive account registration | create_account() |
| ATM Operations | Balance, deposit, withdraw, mini-statement, PIN change | balance_inquiry(), deposit(), withdraw(), mini_statement(), change_pin()
|
| Admin Functions | Unlock accounts, view accounts/transactions, refill ATM, change password | admin_unlock_account(), admin_view_all_accounts(), admin_view_atm_cash(), admin_refill_atm(), admin_change_password(), admin_view_transaction()
|
| Menu Systems | ATM menu, admin menu, main menu loops | atm_menu(), admin_menu(), main_menu() |
| Entry Point | Script initialization guard | if __name__ == "__main__" |
Imports & Dependencies
import sqlite3
import os
import re
import hashlib
from datetime import datetime, date
from getpass import getpass
from typing import Dict, Any, Optional, Tuple
from contextlib import contextmanager
| Import | Purpose | Where Used |
|---|---|---|
sqlite3 |
Database operations (connections, cursors, transactions) | All DB helpers; CRUD operations; transaction queries |
os |
Filesystem checks (path existence, directory creation) | Receipt folder creation; implicit CWD assumptions |
re |
Regular expressions for pattern matching | Name validation (re.match(r"^[A-Za-z\s]+$", ...))
|
hashlib |
Cryptographic hashing (SHA-256) | PIN hashing, admin password hashing |
datetime / date |
Timestamps for transactions; date comparisons for daily limits | Transaction records; last_withdraw_date tracking;
daily withdraw calculation
|
getpass |
Masked password input (no echo to terminal) | PIN input, admin password input |
typing |
Type hints for function signatures | Function annotations throughout |
contextlib |
Context manager decorator (@contextmanager) |
get_db_transaction() for transaction safety |
Global State & Configuration
Constants:
DB_FILE = "users.db" # SQLite database filename
MIN_BALANCE = 500 # Minimum account balance (cannot withdraw below)
DEFAULT_DAILY_WITHDRAW_LIMIT = 20000.0 # Per-account daily withdrawal cap
DEFAULT_ATM_CASH_POOL = 1000000.0 # Total ATM cash available
RECEIPTS_FOLDER = "receipts" # Folder for transaction receipts
MAX_NAME_LENGTH = 50 # Name field constraint
MIN_NAME_LENGTH = 2 # Name field constraint
PIN_LENGTH = 4 # PIN is always 4 digits
DISALLOW_SEQUENTIAL = True # Reject PINs like 1234, 4321
DISALLOW_REPEATING = True # Reject PINs like 1111, 2222
Computed Global State:
ADMIN_PASSWORD = hash_password("SecureAdmin@2025")
This constant is computed once at import time and stored. The default admin credential is hardcoded in source.
Hidden Coupling:
- Current Working Directory: The script assumes
os.getcwd()is writable. If run from a read-only directory (e.g.,/usr/bin/),init_db()will fail to createusers.dbor thereceipts/folder. - Relative Paths: No absolute path resolution; all paths are relative to CWD. Deploying multiple instances in the same directory will compete for the same database file.
- Salt Reuse: The admin password uses a static salt:
atm_system_secure_salt_2025. This is a weak practice for production—salts should be per-user or randomly generated.
Step-by-Step Walkthrough
Security Utilities Section
Function: hash_password(password: str) -> str
def hash_password(password: str) -> str:
"""Hash a password using SHA-256"""
salt = "atm_system_secure_salt_2025"
return hashlib.sha256((password + salt).encode()).hexdigest()
- Purpose: Hash a plaintext password (used for admin password storage).
- Parameters:
password(string, no validation on length/content). - Return: Hexadecimal SHA-256 digest (64 characters, lowercase).
- Precondition: None (accepts any string).
- Postcondition: Deterministic; same password always produces same hash.
- Side Effects: None.
- Logic:
- Prepend static salt to password.
- Encode string as UTF-8 bytes.
- Compute SHA-256 hash.
- Return hexadecimal representation.
- Edge Cases: Empty password accepted (produces hash of salt alone); no length enforcement.
- Complexity: O(n) where n is password length (SHA-256 is constant-time hash function).
Issue: Static salt (atm_system_secure_salt_2025)
is weak. A real system
should use secrets module or random per-user salts.
Function: hash_pin(pin: str) -> str
def hash_pin(pin: str) -> str:
"""Hashes the PIN using SHA_256 for secure storage."""
return hashlib.sha256(pin.encode()).hexdigest()
- Purpose: Hash user PIN for database storage (no plaintext PINs).
- Parameters:
pin(assumed 4 digits, validated before calling). - Return: 64-character hexadecimal SHA-256 digest.
- Note: PIN is hashed without salt, which is acceptable for PINs (unlike passwords) because PIN entropy is low (10,000 possibilities) and salt adds negligible security.
Function: validate_pin_strength(pin: str) -> Tuple[bool, str]
def validate_pin_strength(pin: str) -> Tuple[bool, str]:
"""Validate PIN against security policies."""
if len(pin) != PIN_LENGTH:
return False, f"PIN must be {PIN_LENGTH} digits."
if not pin.isdigit():
return False, "PIN must be numeric."
if DISALLOW_REPEATING and len(set(pin)) == 1:
return False, "PIN cannot have all repeating digits (e.g., 1111)"
if DISALLOW_SEQUENTIAL:
is_ascending = all(int(pin[i]) == int(pin[i-1]) + 1 for i in range(1, len(pin)))
is_descending = all(int(pin[i]) == int(pin[i-1]) - 1 for i in range(1, len(pin)))
if is_ascending or is_descending:
return False, "PIN cannot be sequential (e.g., 1234, 4321)"
return True, ""
- Purpose: Enforce PIN policies (length, digits-only, no repeating/sequential patterns).
- Return:
(is_valid: bool, error_message: str)tuple. - Logic:
- Check length is exactly
PIN_LENGTH(4). - Check all characters are digits (
isdigit()). - Check not all digits are identical (
len(set(pin)) == 1). - Check not ascending sequence (e.g., 1234): compare each digit to previous + 1.
- Check not descending sequence (e.g., 4321): compare each digit to previous - 1.
- Edge Cases: For 4-digit PIN,
range(1, 4)checks indices 1, 2, 3 against indices 0, 1, 2; this correctly validates all adjacent pairs. - Complexity: O(1) for fixed PIN length of 4..
Function: sanitize_name(name: str) -> Tuple[bool, str, str]
def sanitize_name(name: str) -> Tuple[bool, str, str]:
"""Sanitize and validate user name."""
name = " ".join(name.strip().split()) # Collapse whitespace
if len(name) < MIN_NAME_LENGTH:
return False, "", f"Name must be at least {MIN_NAME_LENGTH} characters."
if len(name) > MAX_NAME_LENGTH:
return False, "", f"Name must be at least {MAX_NAME_LENGTH} characters."
if not re.match(r"^[A-Za-z\s]+$", name):
return False, "", "Name can only contain letters and spaces."
return True, name, ""
- Purpose: Clean and validate user names (prevent injection, enforce policy).
- Return:
(is_valid: bool, sanitized_name: str, error_message: str). - Logic:
- Collapse multiple spaces into single space.
- Validate length (2–50 characters).
- Validate character set (A–Z, a–z, spaces only).
- Sanitization: Removes extra whitespace; does not remove/escape special characters (regex enforces alphanumeric + space).
- Precondition: None.
- Edge Cases:
- All-space input: After
.strip(), becomes empty, fails MIN_NAME_LENGTH check. - Unicode names (e.g., "José", "李"): Rejected by regex (ASCII-only).
- Regex pattern
^[A-Za-z\s]+$requires entire string to match.
- Complexity: O(n) where n is name length (regex matching + collapse).
Function: mask_account_number(account_number: str) -> str
def mask_account_number(account_number: str) -> str:
"""Mask account number for receipts (e.g., 1000000000 -> ****000000)"""
if len(account_number) <= 4:
return "****"
return "*" * (len(account_number) - 4) + account_number[-4:]
- Purpose: Hide most of account number on receipts (PII protection).
- Logic: Mask all but last 4 digits with asterisks.
- Edge Cases: If account number ≤ 4 characters, return all asterisks (prevents underflow in slicing).
- Complexity: O(n) for string concatenation.
Database Helpers
Context Manager:
get_db_transaction()
@contextmanager
def get_db_transaction():
conn = sqlite3.connect(DB_FILE)
conn.row_factory = sqlite3.Row
cur = conn.cursor()
try:
yield conn, cur
except Exception as e:
conn.rollback()
raise e
finally:
conn.close()
- Purpose: Encapsulate database transaction lifecycle (connection open ⟶ yield for work ⟶ commit/rollback ⟶ close).
- Return Tuple of (
conn, cur). - Usage Pattern:
with get_db_transaction() as (conn, cur):
cur.execute("UPDATE users SET balance = ? WHERE account_number = ?", (...))
# Auto-commits on successful exit; auto-rolls back on exception
- Behavior:
- Opens connection to
DB_FILE. - Sets
row_factory = sqlite3.Row(allows row[column_name] access, not just row[index]). - On normal exit: commits changes.
- On exception: rolls back changes and re-raises exception.
- Finally block: Always closes connection.
- Atomicity: Provides ACID guarantees within the block; either all SQL in block succeeds or all rolls back.
- Complexity: O(1) overhead; DB work is O(data).
Function: get_db_connection()
def get_db_connection():
conn = sqlite3.connect(DB_FILE)
conn.row_factory = sqlite3.Row
return conn
- Purpose: Simple connection factory for read-only or explicit transaction control.
- Note: Returns raw connection; caller must manually
.close()to avoid resource leak. - Comparison: Unlike
get_db_transaction(), this does not auto-commit; useful for SELECT-only queries.
Function:
init_db()
def init_db():
conn = get_db_connection()
cur = conn.cursor()
# CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS users (...)
# CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS transactions (...)
# CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS settings (...)
cur.execute("SELECT COUNT(*) AS count FROM settings")
if cur.fetchone()["count"] == 0:
cur.execute("INSERT INTO settings (...) VALUES(1, ?, ?, ?)",
(DEFAULT_ATM_CASH_POOL, DEFAULT_DAILY_WITHDRAW_LIMIT, ADMIN_PASSWORD))
conn.commit()
conn.close()
if not os.path.exists(RECEIPTS_FOLDER):
os.makedirs(RECEIPTS_FOLDER)
- Purpose: Initialize SQLite schema and default settings on first run.
- Tables Created:
- Users: account_number (PK), name, pin_hash, balance, locked (0/1), failed_attempts, created_at (ISO timestamp), last_withdraw_date (ISO date or NULL).
- transactions: id (auto-increment PK), account_number (FK), type (string), amount (real), datetime (ISO), balance_after (real).
- settings: id (1, singleton), atm_cash_pool (real), daily_withdraw_limit (real), admin_password_hash.
- Idempotency:
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTSprevents errors on re-run. - Side Effects:
- Creates database file if missing.
- Inserts default settings row (only if none exist).
- Creates
receipts/directory.
- Potential Issue: No error handling for filesystem permission errors (e.g., CWD not writable).
Storage & Utility Functions
Function:
generate_account_number() -> str
def generate_account_number() -> str:
# Open a SQLite connection using the project helper (caller must close it).
conn = get_db_connection()
# Create a cursor object used to execute SQL queries.
cur = conn.cursor()
# Start from a fixed 10-digit base account number (1,000,000,000).
# The function increments this value until it finds a number not present in the DB.
base = 1000000000 # 10-digit starting point
# Loop until an unused account number is found.
# Note: there is no upper bound here, so it can theoretically loop indefinitely.
while True:
# Convert the current candidate number to string (account numbers are stored as TEXT).
acc = str(base)
# Check whether this account number already exists in the users table.
# Parameterized query prevents SQL injection.
cur.execute("SELECT 1 FROM users WHERE account_number = ?", (acc,))
# If no row is returned, the account number is available.
if cur.fetchone() is None:
# Close DB connection to avoid resource leaks.
conn.close()
# Return the unique account number.
return acc
# Otherwise, try the next sequential number.
base += 1
- Purpose: Generate a unique 10-digit account number.
- Logic: Start at 1 billion; check if exists in DB; increment until unused number found.
- Return: String representation of account number (e.g., "1000000000").
- Complexity: O(c) where c is the count of existing accounts (worst case: iterate until hole found).
- Issue:
- No upper bound: If all numbers from 1e9 to 2e9 − 1 are taken, loop runs indefinitely.
- Race condition: Two concurrent calls could generate the same number if both check and insert in sequence.
- Connection leak:If exception occurs after opening
conn, connection is not closed.
Function:
get_user(account_number: str) -> Optional[Dict[str, Any]]
def get_user(account_number: str) -> Optional[Dict[str, Any]]:
# Open a SQLite connection using the project helper (creates users.db connection).
# Note: this returns a raw connection, so it must be closed manually.
conn = get_db_connection()
# Create a cursor object used to execute SQL queries.
cur = conn.cursor()
# Fetch the user row for the given account number.
# Using a parameterized query ("?") prevents SQL injection.
cur.execute("SELECT * FROM users WHERE account_number = ?", (account_number,))
# Read one matching record (account_number is expected to be unique / primary key).
# If no record exists, fetchone() returns None.
row = cur.fetchone()
# Close the connection to avoid leaking DB resources.
conn.close()
# If a row exists, convert it into a normal Python dict and return it.
# This works because the connection uses sqlite3.Row row_factory (dict-like row object).
# If row is None, return None to signal "user not found".
return dict(row) if row else None
- Purpose: Retrieve user record by account number.
- Return: Dictionary of user fields, or None if not found.
- Safety: Uses parameterized query (
?placeholder), immune to SQL injection. - Note:
sqlite3.Rowsupportsdict()conversion due to row_factory setting. - Complexity: O(1) if account_number is PK (indexed), O(n) otherwise.
Function:
update_user(user: Dict[str, Any]) -> None
def update_user(user: Dict[str, Any]) -> None:
# Update an existing user's record in the SQLite database using a safe transaction.
# Using get_db_transaction() ensures:
# - All changes inside the block are committed together on success.
# - Any exception causes an automatic rollback (prevents partial updates).
# - The DB connection is always closed properly.
with get_db_transaction() as (conn, cur):
# Execute a parameterized UPDATE statement to modify the user row identified by account_number.
# Parameterized queries ("?") prevent SQL injection and ensure correct value escaping.
cur.execute("""
UPDATE users
SET name = ?, -- Update user's name (sanitized string).
pin_hash = ?, -- Update stored PIN hash (SHA-256 hash of PIN).
balance = ?, -- Update current account balance (float).
locked = ?, -- Update lock status (stored as 0/1 integer in SQLite).
failed_attempts = ?, -- Update failed login attempts counter (integer).
last_withdraw_date = ? -- Update last withdrawal date (ISO date string or NULL).
WHERE account_number = ? -- Identify which user row to update (primary key).
""", (
user["name"], # Must exist in dict; otherwise KeyError.
user["pin_hash"], # Must exist in dict; otherwise KeyError.
user["balance"], # Must exist in dict; otherwise KeyError.
int(user.get("locked", False)), # Convert bool -> 0/1 for SQLite INTEGER column.
user.get("failed_attempts", 0), # Default 0 if key missing (avoids KeyError).
user.get("last_withdraw_date"), # Date string (YYYY-MM-DD) or None.
user["account_number"] # Must exist; used to locate the row to update.
))
- Purpose: Update user record in DB (in-place modification).
- Parameters: Dictionary with at least
account_numberkey; other keys must exist or have defaults. - Type Coercions:
int(user.get("locked", False))converts boolean to 0/1 for SQLite. - Precondition:
userdict must contain all required keys; no validation performed. - Side Effect: Modifies DB; committed automatically by context manager.
- Complexity: O(1).
Function:
create_user_record(account_number: str, name: str, pin_hash: str, initial_deposit: float) -> None
def create_user_record(account_number: str, name: str, pin_hash: str, initial_deposit: float) -> None:
# Create a DB transaction context so the INSERT is atomic:
# it will COMMIT automatically if everything succeeds, or ROLLBACK if an exception occurs.
with get_db_transaction() as (conn, cur):
# Insert a brand-new user row into the `users` table.
# - account_number: unique account ID (stored as TEXT, primary key)
# - name: already validated/sanitized before calling this function
# - pin_hash: SHA-256 hash of the user’s PIN (never store raw PIN)
# - initial_deposit: starting balance for the account
# - locked = 0: account starts unlocked
# - failed_attempts = 0: no failed login attempts initially
# - created_at = current timestamp in ISO format (e.g., "2026-01-08T09:29:00...")
# - last_withdraw_date = NULL: no withdrawals done yet
cur.execute(
"""INSERT INTO users (...) VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, 0, 0, ?, NULL)""",
(account_number, name, pin_hash, initial_deposit, datetime.now().isoformat())
)
# No return value: success means the user record is now persisted in SQLite.
- Purpose: Insert new user into DB.
- Parameters: Account number, name (already sanitized), pin hash, initial balance.
- Auto-Values:
locked = 0,failed_attempts = 0,last_withdraw_date = NULL. - Timestamp:
created_atis ISO format timestamp of insertion. - Precondition: Caller must ensure account_number is unique (no duplicate check here).
- Side Effect: Inserts row; auto-commits.
- Complexity: O(1).
Function:
verify_pin(user: Dict[str, Any], pin: str) -> bool
def verify_pin(user: Dict[str, Any], pin: str) -> bool:
# Hash the entered PIN and compare it with the stored PIN hash for this user.
# Returns True if they match (correct PIN), otherwise False.
return user["pin_hash"] == hash_pin(pin)
- Purpose: Constant-time PIN verification (compares hashes, not plaintext).
- Returns: True if PIN matches stored hash.
- Notes: Comparison is not constant-time (Python string
==is vulnerable to timing attacks), but acceptable for 4-digit PINs.
Function:
is_account_locked(user: Dict[str, Any]) -> bool
def is_account_locked(user: Dict[str, Any]) -> bool:
# Returns True if the user's account is marked as locked (locked = 1/True), else False.
return bool(user.get("locked", 0))
- Purpose: Check if a user's account is locked.
- Returns: True if user["locked"] is truthy (1, True, etc.).
Function:
increment_failed_attempts(user: Dict[str, Any]) -> None
def increment_failed_attempts(user: Dict[str, Any]) -> None:
# Increase the failed login attempt counter by 1 (start from 0 if not present).
user["failed_attempts"] = user.get("failed_attempts", 0) + 1
# If the user has reached 3 or more failed attempts, mark the account as locked.
if user["failed_attempts"] >= 3:
user["locked"] = True
# Save the updated user state back to the database.
update_user(user)
- Purpose: Increment failed login counter; lock account after 3 attempts.
- Side Effects: Modifies user dict in-place and persists to DB.
- Logic: If attempts reach 3, set
locked = True. - Precondition: User dict must be mutable.
Function:
increment_failed_atrecord_transaction(account_number: str, tx_type: str, amount: float, balance_after: float) -> None
def record_transaction(account_number: str, tx_type: str, amount: float, balance_after: float) -> None:
# Open a database transaction and get a connection and cursor.
with get_db_transaction() as (conn, cur):
# Insert a new transaction row with account number, type, amount,
# current timestamp, and balance after the transaction.
cur.execute("""
INSERT INTO transactions (account_number, type, amount, datetime, balance_after)
VALUES(?, ?, ?, ?, ?)
""", (account_number, tx_type, amount, datetime.now().isoformat(), balance_after))
# Return the auto-generated transaction ID of the inserted row.
return cur.lastrowid # [file:96]
- Purpose:Log a transaction (balance inquiry, deposit, withdraw, PIN change, etc.).
- Parameters: Account number, transaction type (string, no enum), amount, balance after transaction.
- Return:Last inserted row ID (transaction ID, used for receipts).
- Note: Type is freeform string (e.g., "DEPOSIT", "WITHDRAW", "BALANCE", "PIN CHANGE", "ADMIN_UNLOCK").
- Timestamp: ISO format at time of insertion.
- Complexity: O(1).
Function:
get_today_withdrawn_amount(account_number: str) -> float
def get_today_withdrawn_amount(account_number: str) -> float:
# Look up the user record for this account number.
user = get_user(account_number)
# If the account does not exist, treat today's withdrawn amount as zero.
if not user:
return 0.0
# Get the date of the last withdrawal stored on the user record.
last_withdraw_date = user.get("last_withdraw_date")
# Get today’s date as an ISO string (YYYY-MM-DD).
today = date.today().isoformat()
# If the last withdrawal was not today, then nothing has been withdrawn today.
return 0.0 if last_withdraw_date != today else _sum_today_withdrawals(account_number)
def _sum_today_withdrawals(account_number: str) -> float:
# Open a database connection and create a cursor for executing queries.
conn = get_db_connection()
cur = conn.cursor()
# Sum all WITHDRAW transactions for this account whose date is today.
cur.execute("""
SELECT COALESCE(SUM(amount), 0) AS total
FROM transactions
WHERE account_number = ? AND type = 'WITHDRAW' AND date(datetime) = date('now', 'localtime')
""", (account_number,))
# Get the resulting row (or None if there are no matching transactions).
row = cur.fetchone()
# Close the connection to free database resources.
conn.close()
# Convert the summed amount to float and return it (0.0 if row is missing).
return float(row['total'] if row else 0.0)
- Purpose: Calculate total withdrawn today for daily limit enforcement.
- Logic:
- Check if
last_withdraw_dateequals today; if not, return 0.0 (no withdrawals today). - If yes, sum all WITHDRAW transactions from today.
- SQL Note:
date('now', 'localtime')uses SQLite's time functions (locale-aware). - Return: Floating-point balance (sum or 0.0).
- Complexity: O(n) where n is transaction count today (full table scan if no index on account_number + type + date).
Function:
get_settings() -> Dict[str, Any]
def get_settings() -> Dict[str, Any]:
# Open a database connection and create a cursor for running queries.
conn = get_db_connection()
cur = conn.cursor()
# Fetch the settings row with primary key id = 1 (the single config row).
cur.execute("SELECT * FROM settings WHERE id = 1")
row = cur.fetchone()
# Close the database connection after the query is done.
conn.close()
# If a settings row exists, convert it to a dictionary and return it.
if row:
return dict(row)
# If no settings row is found, return a default settings dictionary.
return {
"atm_cash_pool": 0.0,
"daily_withdraw_limit": DEFAULT_DAILY_WITHDRAW_LIMIT,
"admin_password_hash": ADMIN_PASSWORD,
}
- Purpose: Retrieve ATM-wide settings (cash pool, withdrawal limit, admin password).
- Return: Dictionary; defaults to zero cash pool if settings not found (catastrophic).
- Precondition: Settings row (id=1) should exist after
init_db().
Function:
update_atm_cash_pool(new_amount: float) -> None
def update_atm_cash_pool(new_amount: float) -> None:
# Open a database transaction and get a connection and cursor.
with get_db_transaction() as (conn, cur):
# Update the ATM's total available cash value to the new_amount in the settings table.
cur.execute("UPDATE settings SET atm_cash_pool = ? WHERE id = 1", (new_amount,))
- Purpose: Update ATM cash pool (decremented on withdrawals, incremented on admin refill).
- Complexity: O(1).
Receipt Generation
Function:
generate_receipt(account_number: str, tx_id: int, tx_type: str, amount: float, balance_after: float, additional_info:
str = "") -> str
def generate_receipt(account_number: str, tx_id: int, tx_type: str,
amount: float, balance_after: float,
additional_info: str = "") -> str:
# Look up the full user record for this account number (used for name, etc.).
user = get_user(account_number)
# Capture the current date and time for the receipt timestamp.
timestamp = datetime.now()
# Mask the account number so only the last few digits are visible on the receipt.
masked_account = mask_account_number(account_number)
# Build a unique receipt file name using account number, timestamp, and transaction ID.
filename = f"receipt_{account_number}_{timestamp.strftime('%d%m%Y_%H%M%S')}_{tx_id}.txt"
# Create the full path to the receipt file inside the receipts folder.
filepath = os.path.join(RECEIPTS_FOLDER, filename)
# Compose the receipt content as a multi-line formatted string.
# It typically includes masked account, user name, type, amount, balance, timestamp, etc.
receipt = f"""
{"=" * 50}
ATM TRANSACTION RECEIPT
...
"""
# Open the file in write mode with UTF-8 encoding and write the receipt text to disk.
with open(filepath, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write(receipt)
# Return just the receipt file name so the caller can display or log it.
return filename
- Purpose: Generate and write text receipt file to disk..
- parameters: Account number, transaction ID, type, amount, balance, optional additional info.
- Return: Filename (not full path).
- Filename Format:
receipt_{account_number}_{DDmmYYYY_HHMMSS}_{tx_id}.txt. - Content Formatted text with transaction details, masked account number, timestamp.
- Side Effects:
- Reads user record (to get name).
- Writes file to
receipts/folder.
- Precondition:
receipts/folder must exist (created by init_db()). - Error Handling: No error handling; will raise
FileNotFoundErrororPermissionErrorif folder missing or not writable. - Complexity: O(1) for string formatting + O(file_size) for write.
Authentication Functions
Function:
verify_admin_password() -> bool
def verify_admin_password() -> bool:
# Load ATM settings from the database (includes stored admin password hash).
settings = get_settings()
# Prompt the admin to enter the password without showing it on the screen.
password = getpass("Enter admin password: ")
# Hash the entered password using the same function used when storing it.
input_hash = hash_password(password)
# Compare the entered password's hash with the stored hash.
# If they do not match, show an error and indicate failure.
if input_hash != settings['admin_password_hash']:
print('Incorrect admin password.')
return False
# If the hashes match, the admin is successfully authenticated.
return True
- Purpose: Verify admin password attempt against stored hash.
- Return: True if password matches; False otherwise.
- Input: Masked via
getpass()(no echo to terminal). - hashing: Uses
hash_password()with static salt. - Precondition: Settings row must exist.
- Complexity: O(1).
Function:
login() -> Tuple[Optional[str], Optional[Dict[str, Any]]]
def login() -> Tuple[Optional[str], Optional[Dict[str, Any]]]:
# Show a simple heading for the login process.
print("\n=== Login ===")
# Ask the user for their account number and remove extra spaces.
acc = input("Enter account number: ").strip()
# Look up the user record for this account number.
user = get_user(acc)
# If no such account exists, stop and signal failed login.
if not user:
print("Account not found.")
return None, None
# If the account is already locked, do not allow login.
if is_account_locked(user):
print("Account is locked...")
return None, None
# Allow up to 3 attempts to enter the correct PIN.
for _ in range(3):
# Read the PIN securely (hidden input) and strip spaces.
pin = getpass("Enter 4-digit PIN: ").strip()
# Reject non‑numeric or wrong‑length PIN input and count as a failed attempt.
if not pin.isdigit() or len(pin) != 4:
print("PIN must be a 4-digit number.")
increment_failed_attempts(user)
# If the PIN matches the stored hash, login succeeds.
elif verify_pin(user, pin):
print("Login successful.")
reset_failed_attempts(user) # Clear failed-attempt counter.
return acc, get_user(acc) # Return account number and fresh user data.
# If the PIN is numeric and 4 digits but incorrect, handle as failed attempt.
else:
print("Incorrect PIN.")
increment_failed_attempts(user)
user = get_user(acc) # Reload user to see updated lock status.
# Compute how many attempts are left (out of 3).
remaining = 3 - user["failed_attempts"]
# If there are attempts left and the account is not yet locked, show remaining attempts.
if remaining > 0 and not user["locked"]:
print("Attempts remaining:", remaining)
else:
# If no attempts remain or the account was locked, inform the user.
print("Account locked...")
# If control reaches here inside the loop, treat it as a failed login.
return None, None
# Fallback return if the loop exits without a successful login.
return None, None
e
- Purpose: Authenticate user by account number + 4-digit PIN.
- Return:
(account_number, user_dict)on success;(None, None)on failure. - Flow:
- Prompt for account number; check if exists.
- Check if account already locked.
- Loop up to 3 times for PIN attempts.
- Validate PIN format (4 digits).
- Hash PIN and compare to stored hash.
- On success: reset failed attempts, refresh user data, return.
- On failure: increment failed attempts (may lock account), reload user, display remaining attempts.
- Edge Cases:
- Invalid PIN format (not 4 digits): Still counts as attempt and increments counter.
- Account locked during loop: Condition checked only after each failed attempt, so loop may still run 3 times.
- Security: PIN masked via
getpass(). - Complexity: O(3) iterations + O(1) per DB query = O(1).
Account Creation
Function:
create_account() -> None
def create_account() -> None:
# Show section heading for account creation.
print("\n=== Create Account ===")
# Ask for the user's name until a valid, sanitized name is entered.
while True:
name = input("Enter your name: ").strip().capitalize()
is_valid, sanitize_named, error = sanitize_name(name)
if not is_valid:
print(f"{error}.") # Explain why the name is invalid.
continue # Ask again if invalid.
break # Exit loop when name is valid.
# Ask the user to set a PIN and confirm it, repeating until it is valid.
while True:
pin = getpass("Set a 4-digit numeric PIN: ")
confirm = getpass("Confirm PIN: ")
if pin != confirm:
print("PINs do not match. Try again.")
continue # Ask again if confirmation fails.
# Check the PIN strength against the defined rules.
is_valid, error = validate_pin_strength(pin)
if not is_valid:
print(f"{error}") # Show why the PIN is weak/invalid.
print("PIN Policy: ...")
continue # Ask for a new PIN if invalid.
break # Exit loop when PIN is valid.
# Ask for the initial deposit amount until a valid numeric value is given.
while True:
try:
amount = float(input(f"Enter initial deposit (min {MIN_BALANCE}):"))
if amount < MIN_BALANCE:
print(f"Minimum initial deposit is {MIN_BALANCE}.")
continue # Enforce minimum starting balance.
break # Exit loop when amount is valid.
except ValueError:
print("Invalid amount. Please enter a numeric value.") # Handle non-numeric input.
# Securely hash the PIN before storing it.
pin_hash = hash_pin(pin)
# Generate a new unique account number for the user.
account_number = generate_account_number()
# Insert the new user into the database with the given details.
create_user_record(account_number, sanitize_named, pin_hash, amount)
# Record the initial deposit as a transaction for audit/history.
tx_id = record_transaction(account_number, "DEPOSIT", amount, amount)
# Create a receipt file documenting the account creation and initial deposit.
receipt_file = generate_receipt(
account_number,
tx_id,
"ACCOUNT CREATION - INITIAL DEPOSIT",
amount,
amount,
"Welcome to our ATM service!"
)
# Print a visual separator and success message to the user.
print("\n" + "=" * 50)
print("\nACCOUNT CREATED SUCCESSFULLY!")
...
- Purpose: Register a new user account interactively.
- Flow:
- Prompt for name (loop until valid and sanitized).
- Prompt for PIN (loop until valid and confirmed).
- Prompt for initial deposit (loop until valid amount ≥ MIN_BALANCE).
- Generate account number.
- Create user record in DB.
- Record initial deposit as transaction.
- Generate receipt file.
- Display confirmation with account number.
- Side Effects:
- Writes to DB (users, transactions tables).
- Writes receipt file to disk.
- Prints confirmation.
- Precondition: DB must be initialized.
- Complexity: O(1) for logic + O(account count) for unique account generation.
ATM Operations
Function:
balance_inquiry(account_number: str) -> None
def balance_inquiry(account_number: str) -> None:
# Look up the user record for the given account number.
user = get_user(account_number)
# If no user exists with this account number, show a message and stop.
if not user:
print("User not found.")
return
# Print a simple formatted header for the balance inquiry screen.
print("\n" + "=" * 50)
print("BALANCE INQUIRY")
print("=" * 50)
# Show the current balance with two decimal places.
print(f"\nCurrent balance: {user['balance']:.2f}")
print("=" * 50)
# Log this balance check as a transaction (amount is 0.0, balance stays the same).
tx_id = record_transaction(account_number, "BALANCE", 0.0, user["balance"])
- Purpose: Display current account balance and log a BALANCE inquiry transaction.
- Side Effects: Inserts BALANCE record in transactions table (useful for audit trail).
- Complexity: O(1).
Function:
deposit(account_number: str) -> None
def deposit(account_number: str) -> None:
# Look up the user record for this account number.
user = get_user(account_number)
# If no user exists, stop the operation.
if not user:
print("User not found.")
return
# Print a simple section header for the deposit screen.
print("\n" + "=" * 50)
print(" DEPOSIT")
print("=" * 50)
# Show the user's current balance.
print(f"\nCurrent balance: {user['balance']:.2f}")
try:
# Ask the user how much money to deposit and convert it to a number.
amount = float(input("Enter deposit amount: "))
except ValueError:
# If the input is not a valid number, cancel the deposit.
print("Invalid amount.")
return
# Reject zero or negative deposit amounts.
if amount <= 0:
print("Amount must be positive.")
return
try:
# Start a database transaction to keep updates consistent.
with get_db_transaction() as (conn, cur):
# Calculate the new balance after adding the deposit amount.
new_balance = user['balance'] + amount
# Update the user's balance in the users table.
cur.execute(
"UPDATE users SET balance = ? WHERE account_number = ?",
(new_balance, account_number)
)
# Insert a new transaction record describing this deposit.
cur.execute(
"INSERT INTO transactions (...) VALUES (...)",
(account_number, "DEPOSIT", amount, datetime.now().isoformat(), new_balance)
)
# Get the auto-generated transaction ID for the new record.
tx_id = cur.lastrowid
# Create a receipt file for this deposit and get its filename.
receipt_file = generate_receipt(
account_number, tx_id, "DEPOSIT", amount, new_balance
)
# If everything succeeded, inform the user and show the new balance and receipt file name.
print("\nDeposit successful!")
print(f"New Balance: {new_balance:.2f}")
print(f"Receipt saved: {receipt_file}")
print("=" * 50)
except Exception as e:
# If anything goes wrong during the transaction, report the error
# and let the user know their balance was not changed.
print(f"Transaction failed: {str(e)}")
print("Your balance has not been changed.")
- Purpose: Deposit funds into account.
- Flow:
- Prompt for amount.
- Validate amount > 0.
- Within transaction block: update balance, insert transaction record, generate receipt.
- On exception: catch and display error; transaction auto-rolls back.
- Atomicity: All three operations (balance update, transaction insert, receipt write) happen together or not at all.
- Note: Receipt write is outside the transaction block (not rolled back if receipt file write fails, but balance/transaction update succeeds).
- Complexity: O(1).
Function:
withdraw(account_number: str) -> None
def withdraw(account_number: str) -> None:
# Look up the user by account number; stop if the account does not exist.
user = get_user(account_number)
if not user:
print("User not found.")
return
# Load global ATM settings (total cash in ATM and per-account daily withdraw limit).
settings = get_settings()
atm_cash = settings["atm_cash_pool"]
daily_limit = settings["daily_withdraw_limit"]
# Print a formatted header and current account/ATM info for the user.
print("\n" + "=" * 70)
print("WITHDRAW")
print("=" * 70)
print(f"\nCurrent balance: {user['balance']:.2f}")
print(f"Minimum balance: {MIN_BALANCE:.2f}")
print(f"Available: {max(0, user['balance'] - MIN_BALANCE):.2f}")
print(f"Daily withdraw limit: {daily_limit:.2f}")
print(f"ATM cash: {atm_cash:.2f}")
# Ask the user how much they want to withdraw, handling non-numeric input.
try:
amount = float(input("\nEnter withdrawal amount: "))
except ValueError:
print("Invalid amount.")
return
# Reject zero or negative amounts.
if amount <= 0:
print("Amount must be positive.")
return
# Ensure the withdrawal does not reduce the balance below the required minimum.
if user['balance'] - amount < MIN_BALANCE:
max_withdrawable = max(0.0, user['balance'] - MIN_BALANCE)
print(f"Cannot withdraw. Minimum balance of {MIN_BALANCE:.2f} must remain...")
return
# Check that the user does not exceed the per-day withdrawal limit.
today_withdraw = get_today_withdrawn_amount(account_number)
if today_withdraw + amount > daily_limit:
remaining = max(0.0, daily_limit - today_withdraw)
print("Cannot withdraw this amount due to daily limit...")
return
# Ensure the ATM itself has enough cash to dispense this amount.
if amount > atm_cash:
print("ATM does not have enough cash...")
return
# Perform the withdrawal in a database transaction so all updates succeed or fail together.
try:
with get_db_transaction() as (conn, cur):
# Compute the new user balance and update the user record with balance and today's date.
new_balance = user['balance'] - amount
today = date.today().isoformat()
cur.execute(
"UPDATE users SET balance = ?, last_withdraw_date = ? WHERE account_number = ?",
(new_balance, today, account_number),
)
# Decrease the ATM cash pool by the withdrawn amount and update settings.
new_atm_cash = atm_cash - amount
cur.execute(
"UPDATE settings SET atm_cash_pool = ? WHERE id = 1",
(new_atm_cash,),
)
# Insert a transaction record describing this withdrawal.
cur.execute(
"INSERT INTO transactions (...) VALUES (...)",
(account_number, "WITHDRAW", amount, datetime.now().isoformat(), new_balance),
)
tx_id = cur.lastrowid
# Build extra info for the printed receipt (ATM cash and today's total withdrawn).
additional_info = (
f"ATM Cash After: {new_atm_cash:.2f}\n"
f"Daily Withdraw: {today_withdraw + amount:.2f}"
)
# Generate a text receipt file for this withdrawal.
receipt_file = generate_receipt(
account_number, tx_id, "WITHDRAW", amount, new_balance, additional_info
)
# Inform the user that the withdrawal succeeded and show balances.
print(f"{amount:.2f} Withdrawn successfully...")
print(f"New balance: {new_balance:.2f}") # BUG: should display new_balance instead
print(f"ATM Cash Remaining: {new_atm_cash:.2f}")
print("=" * 70)
except Exception as e:
# If anything goes wrong, the transaction is rolled back and the user is notified.
print(f"Transaction failed and rolled back: {str(e)}")
print("Your balance and ATM cash have not been changed.")
- Purpose: Withdraw funds from account with multi-layered constraint checks.
- Constraints Enforced:
- Amount > 0.
- Balance after withdrawal ≥ MIN_BALANCE (500).
- Daily withdrawal total ≤ daily_limit (20000 per settings).
- ATM has sufficient cash.
- Atomicity: User balance, ATM cash pool, and transaction record all updated within single transaction block.
- Updates:
- User balance and
last_withdraw_date. - ATM cash pool (decremented).
- Transaction record (WITHDRAW entry).
- Receipt file (outside transaction, potential orphan if write fails).
- Complexity: O(1) for logic + O(n) for daily withdraw sum query.
Function:
mini_statement(account_number: str) -> None
def mini_statement(account_number: str) -> None:
# Open a database connection and create a cursor for executing queries.
conn = get_db_connection()
cur = conn.cursor()
# Fetch the 5 most recent transactions for this account, newest first.
cur.execute("""
SELECT datetime, type, amount, balance_after
FROM transactions
WHERE account_number = ?
ORDER BY id DESC
LIMIT 5
""", (account_number,))
rows = cur.fetchall()
conn.close() # Close the connection after reading data.
# Print header for the mini statement section.
print("\n" + "=" * 70)
print("\nMINI STATEMENT (Last 5 Transactions)")
print("\n" + "=" * 70)
# If there are no transactions, inform the user and exit the function.
if not rows:
print("No Transactions found.")
return
# Loop through each transaction and print date, type, amount, and balance after.
for tx in rows:
print(f"[{tx['datetime']}] {tx['type']} "
f"Amount: {tx['amount']:.2f} | Balance: {tx['balance_after']:.2f}")
# Print closing line for visual separation.
print("\n" + "=" * 70)
- Purpose: Display last 5 transactions for account.
- Return: None; prints to console.
- Sorting:
ORDER BY id DESC(most recent first). - Complexity: O(log n) for index lookup + O(5) for fetch = O(1).
Function:
change_pin(account_number: str) -> None
def change_pin(account_number: str) -> None:
# Load the user record for the given account number.
user = get_user(account_number)
# If no user exists with this account number, abort the operation.
if not user:
print("User not found.")
return
# Print a header for the Change PIN section.
print("\n" + "=" * 70)
print("CHANGE PIN")
print("\n" + "=" * 70)
# Ask the user for their current PIN (input is hidden).
old_pin = getpass("Enter current PIN: ")
# Verify that the entered current PIN matches the stored PIN hash.
if not verify_pin(user, old_pin):
print("Incorrect current PIN.")
return
# Inform the user that they are about to set a new PIN and show policy info.
print("\nSet new PIN")
print("PIN policy...")
# Loop until the user provides a valid new PIN that meets all requirements.
while True:
# Read new PIN (hidden input) and its confirmation.
new_pin = getpass("Enter new 4-digit PIN: ")
confirm = getpass("Confirm new PIN: ")
# Ensure both entries match.
if new_pin != confirm:
print("PINs do not match. Try again.")
continue
# Prevent reusing the same PIN as before.
if new_pin == old_pin:
print("New PIN cannot be the same as the old PIN.")
continue
# Check the new PIN against the defined strength/format rules.
is_valid, error = validate_pin_strength(new_pin)
if not is_valid:
print(f"{error}")
continue
# New PIN is valid; exit the loop.
break
# Replace the stored PIN hash with the hash of the new PIN.
user["pin_hash"] = hash_pin(new_pin)
# Save the updated user record back to the database.
update_user(user)
# Record a PIN CHANGE transaction (amount 0, balance unchanged).
tx_id = record_transaction(account_number, "PIN CHANGE", 0.0, user["balance"])
# Inform the user that the PIN change was successful.
print("PIN Changed successfully.")
print("=" * 70)
- Purpose: Change user's PIN after verifying old PIN.
- Flow:
- Verify old PIN (exact match with stored hash).
- Prompt for new PIN (loop until valid, confirmed, and different from old).
- Update user record with new PIN hash.
- Log PIN CHANGE transaction.
- Complexity: O(1).
Admin Functions
Function:
admin_unlock_account() -> None
def admin_unlock_account():
# Print a section header for the admin unlock feature.
print("\n" + "=" * 70)
print(" ADMIN UNLOCK ACCOUNT")
print("=" * 70)
# First verify that the caller knows the admin password; abort if not.
if not verify_admin_password():
return
# Fetch all accounts that are currently locked from the database.
conn = get_db_connection()
cur = conn.cursor()
cur.execute(
"SELECT account_number, name, failed_attempts "
"FROM users WHERE locked = 1 ORDER BY account_number"
)
locked_accounts = cur.fetchall()
conn.close()
# If no locked accounts exist, inform the admin and exit.
if not locked_accounts:
print("\nNo locked accounts found.")
return
# Display a simple list of all locked accounts and their failed attempts.
print("Locked Accounts\n-" * 70)
for acc in locked_accounts:
print(f" Account: {acc['account_number']}")
print(f" Name: {acc['name']}")
print(f" Failed Attempts: {acc['failed_attempts']}")
print()
# Ask the admin which account to unlock, or allow unlocking all at once.
account_number = input("Enter account number to unlock (or 'all' for all): ").strip()
if account_number.lower() == "all":
# Bulk unlock: clear the locked flag and failed attempts for every locked account.
with get_db_transaction() as (conn, cur):
cur.execute("UPDATE users SET locked = 0, failed_attempts = 0 WHERE locked = 1")
rows_affected = cur.rowcount
print(f"Unlocked {rows_affected} account(s)")
else:
# Unlock a single specific account.
user = get_user(account_number)
if not user:
print("Account not found.")
return
if not user["locked"]:
print("Account is not locked.")
return
# Reset lock status and failed attempt counter for this user.
user["locked"] = False
user["failed_attempts"] = 0
update_user(user)
# Record an ADMIN_UNLOCK transaction for audit purposes.
record_transaction(account_number, "ADMIN_UNLOCK", 0.0, user['balance'])
# Confirm to the admin that the account has been unlocked.
print(f"\nAccount {account_number} ({user['name']}) has been unlocked...")
- Purpose: Unlock accounts locked due to failed login attempts.
- Authorization: Admin password required.
- Flow:
- Query all locked accounts.
- Display list to admin.
- Prompt for specific account or 'all'.
- Update locked flag and failed_attempts.
- Complexity: O(1) for specific unlock + O(n) for "all" unlock.
Function:
admin_view_all_accounts() -> None
def admin_view_all_accounts():
# Print a formatted header for the admin accounts view section.
print("\n" + "=" * 70)
print(" ADMIN: VIEW ALL ACCOUNTS")
print("=" * 70)
# Ask the admin to enter the admin password; exit if authentication fails.
if not verify_admin_password():
return
# Open a database connection and get a cursor to run SQL queries.
conn = get_db_connection()
cur = conn.cursor()
# Fetch basic details for all users, ordered by account number.
cur.execute(
"SELECT account_number, name, balance, locked, failed_attempts "
"FROM users ORDER BY account_number"
)
accounts = cur.fetchall()
# Close the database connection after fetching the data.
conn.close()
# If there are no user records, inform the admin and exit.
if not accounts:
print("\nNo accounts found.")
return
# Print a table header with fixed-width columns for readability.
print(f"\n{'Account':<15} {'Name':<20} {'Balance':<12} {'Status':<10} {'Failed':<8}")
print("-" * 70)
# Loop through each account and print its details in aligned columns.
for acc in accounts:
# Translate the numeric/boolean locked flag into a human-readable status string.
locked_status = "LOCKED" if acc['locked'] else "ACTIVE"
# Show account number, name, balance (formatted to 2 decimals), status, and failed login attempts.
print(
f"{acc['account_number']:<15} "
f"{acc['name']:<20} "
f"₹{acc['balance']:<10.2f} "
f"{locked_status:<10} "
f"{acc['failed_attempts']:<10}"
)
# Print a footer line and total number of accounts displayed.
print("-" * 70)
print(f"Total Accounts: {len(accounts)}")
print("=" * 70)
- Purpose: Display all accounts in a formatted table.
- Authorization: Admin password required.
- Output: Formatted table with account number, name, balance, lock status, failed attempts.
Function:
admin_view_atm_cash() -> None
def admin_view_atm_cash():
# Print a formatted header for the admin ATM cash view section.
print("\n" + "=" * 70)
print(" ADMIN: ATM CASH POOL")
print("=" * 70)
# Ask the admin to enter the admin password; exit if authentication fails.
if not verify_admin_password():
return
# Load current ATM settings (cash pool and daily withdrawal limit) from the database.
settings = get_settings()
# Show the total cash currently available in the ATM.
print(f"\nCurrent ATM Cash Pool: {settings['atm_cash_pool']:.2f}")
# Show the configured per-account daily withdrawal limit.
print(f"Daily Withdraw Limit: {settings['daily_withdraw_limit']:.2f}")
# Print a closing line to visually end the section.
print("=" * 70)
- Purpose: Display current ATM cash and daily withdraw limit.
Function:
admin_refill_atm() -> None
def admin_refill_atm():
# Print a header for the admin ATM refill screen.
print("\n" + "=" * 70)
print(" ADMIN: REFILL ATM CASH")
print("=" * 70)
# Verify the admin password before allowing any changes.
if not verify_admin_password():
return
# Load current ATM settings, including the cash pool amount.
settings = get_settings()
print(f"\nCurrent ATM Cash Pool: {settings['atm_cash_pool']:.2f}")
try:
# Ask admin how much cash to add to the ATM and convert to float.
amount = float(input("Enter amount to add: "))
except ValueError:
# Handle non‑numeric input gracefully.
print("Invalid amount.")
return
# Ensure the amount is a positive number.
if amount <= 0:
print("Amount must be positive.")
return
# Compute the new total cash pool after adding the given amount.
new_pool = settings['atm_cash_pool'] + amount
# Save the updated cash pool value back to the database/settings.
update_atm_cash_pool(new_pool)
# Show a summary of the update to the admin.
print(f" ATM cash pool updated!")
print(f" Previous: {settings['atm_cash_pool']:.2f}")
print(f" Added: {amount:.2f}")
print(f" New Total: {new_pool:.2f}")
print("=" * 70)
- Purpose: Increase ATM cash pool (simulate ATM refill).
Function:
admin_change_password() -> None
def admin_change_password():
# Print a header for the admin change-password section.
print("\n" + "=" * 70)
print(" ADMIN: CHANGE PASSWORD")
print("=" * 70)
# First verify the current admin password; if wrong, exit the function.
if not verify_admin_password():
return
# Inform admin that a new password will be set.
print("\nSet new admin password...")
# Loop until a valid new password is entered and confirmed.
while True:
# Read the new admin password without echoing it on the screen.
new_password = getpass("Enter new admin password: ")
# Enforce a minimum length of 8 characters.
if len(new_password) < 8:
print("Password must be at least 8 characters.")
continue
# Ask the admin to type the password again to confirm.
confirm = getpass("Confirm new password: ")
# If the two entries do not match, ask again.
if new_password != confirm:
print("Passwords do not match. Try again.")
continue
# Break the loop only when a valid, matching password is provided.
break
# Hash the new password so it is not stored in plain text.
new_hash = hash_password(new_password)
# Open a database transaction to update the stored admin password hash.
with get_db_transaction() as (conn, cur):
cur.execute("UPDATE settings SET admin_password_hash = ? WHERE id = 1", (new_hash,))
# Inform the admin that the password has been changed.
print("\nAdmin password changed successfully!")
print("Please remember your new password!")
print("=" * 70)
- Purpose: Change admin password.
- Validation: Minimum 8 characters; confirmation match required.
Function:
admin_view_transaction() -> None
def admin_view_transaction():
# Print a header for the admin transactions screen.
print("\n" + "=" * 70)
print(" ADMIN: RECENT TRANSACTIONS")
print("=" * 70)
# Ask for and verify the admin password; stop if it is incorrect.
if not verify_admin_password():
return
# Ask how many recent transactions to show; default to 10 if input is invalid.
try:
limit = int(input("\n How many recent transactions to show? (default 10): "))
except ValueError:
limit = 10
# Open a database connection and create a cursor for executing SQL queries.
conn = get_db_connection()
cur = conn.cursor()
# Fetch the most recent transactions joined with user names, limited by the given number.
cur.execute("""
SELECT t.datetime, t.account_number, u.name, t.type, t.amount, t.balance_after
FROM transactions t
JOIN users u ON t.account_number = u.account_number
ORDER by t.id DESC
LIMIT ?
""", (limit, ))
transactions = cur.fetchall()
# Close the database connection once the data is retrieved.
conn.close()
# If there are no transactions, inform the admin and exit.
if not transactions:
print("\nNo transactions found.")
return
# Print table headers for the transaction list.
print(f"\n{'Date/Time':<20} {'Account':<12} {'Name':<15} {'Type':<12} {'Amount':<10} {'Balance':<10}")
print("-" * 90)
# Loop through each transaction and print it in a formatted row.
for tx in transactions:
dt = tx['datetime'][:19] # Trim datetime to a readable format (YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS).
print(f"{dt:<20} {tx['account_number']:<12} {tx['name']:<15} {tx['type']:<12} ₹{tx['amount']:<8.2f} ₹{tx['balance_after']:<8.2f}")
# Print a footer line under the table.
print("-" * 90)
print("=" * 70)
- Purpose: Display recent transactions across all accounts (audit log).
- Join: Transactions joined with users to display names.
- Limit: User can specify how many; defaults to 10.
Menu Systems
Function:
atm_menu(account_number: str) -> None
def atm_menu(account_number: str) -> None:
# Look up the current user from the database using the given account number.
user = get_user(account_number)
# If no user exists for this account number, show a message and exit the menu.
if not user:
print("User not found")
return
# Keep showing the ATM menu until the user chooses to log out.
while True:
# Print a visual separator line and show whose ATM menu this is.
print("\n" + "=" * 70)
print(f" ATM MENU ({user['name']})")
...
# Read the user's menu choice (as a string) and remove extra spaces.
choice = input("Enter your choice (1-6): ").strip()
# If the user chose 1, show their current balance.
if choice == "1":
balance_inquiry(account_number)
# If the user chose 2, start the deposit flow.
elif choice == "2":
deposit(account_number)
# If the user chose 3, start the withdrawal flow.
elif choice == "3":
withdraw(account_number)
# If the user chose 4, show a mini statement of recent transactions.
elif choice == "4":
mini_statement(account_number)
# If the user chose 5, allow them to change their PIN.
elif choice == "5":
change_pin(account_number)
# If the user chose 6, log them out and exit the menu loop.
elif choice == "6":
print("Logging out...")
break
# For any other input, tell the user the choice is invalid.
else:
print("Invalid choice. Please try again.")
# Pause so the user can read the output before showing the menu again.
input("\nPress Enter to continue...")
- Purpose: Main menu for logged-in user (infinite loop until logout).
- Flow: Display menu, read choice (1–6), dispatch to corresponding operation or logout.
Function:
admin_menu() -> None
Similar structure; dispatches to admin functions (1–6) or returns to main menu (7).
Function:
main_menu() -> None
def main_menu() -> None:
# Run the main menu loop until the user chooses to exit.
while True:
# Print a nice header for the main menu.
print("\n" + "=" * 70)
print(" MAIN MENU")
print("=" * 70)
# Show the available top-level options.
print(" 1. Login")
print(" 2. Create Account")
print(" 3. Admin Panel")
print(" 4. Exit")
print("=" * 70)
# Read the user's menu choice as a trimmed string.
choice = input("Enter your choice (1-3): ").strip()
# If user chooses login, perform login and, on success, open the ATM menu.
if choice == "1":
acc, user = login()
if acc and user:
atm_menu(acc)
# If user chooses account creation, run the create-account flow.
elif choice == "2":
create_account()
# If user chooses admin panel, open the admin menu.
elif choice == "3":
admin_menu()
# If user chooses exit, say goodbye and break out of the loop.
elif choice == "4":
print("Thank you for using ATM. Goodbye!")
break
# For any other input, show an error and re-display the menu.
else:
print("Invalid choice. Please try again.")
- Purpose: Entry menu; route to login, account creation, admin panel, or exit.
Entry Point
if __name__ == "__main__": # Run this block only when the script is executed directly, not when imported.
print("\n" + "=" * 70) # Print a visual separator line.
print(" Initializing ATM System...") # Inform the user that initialization is starting.
print("=" * 70) # Print another separator line.
init_db() # Create the database and tables if needed, and prepare the system.
print(" Database initialized successfully.") # Confirm that the database setup is done.
print("Receipts folder created!") # Inform that the receipts directory is ready.
print("Default Admin Password: SecureAdmin@2025") # Show the default admin password.
print("Change it immediately via Admin Panel!") # Warn the user to change the default password.
print("=" * 70) # Print a closing separator line.
main_menu() # Start the main ATM menu loop for user interaction.
- Purpose: Script entry point; only runs if executed directly (not imported).
- Initialization: Calls init_db() to set up schema and defaults.
- Output: Prints initialization banner and default credentials.
Complete Program Flow
Click the link to view a visual guide featuring diagrams and flowcharts that clarify the code explanation.
START
│
├─ main_menu()
│ └─ User selects: 2 (Create Account)
│
├─ create_account()
│ ├─ Input name: "John Doe"
│ │ └─ sanitize_name() ✅
│ │
│ ├─ Input PIN: "1357"
│ │ └─ validate_pin_strength() ✅
│ │
│ ├─ Input deposit: "5000"
│ │ └─ Validate >= MIN_BALANCE ✅
│ │
│ ├─ generate_account_number() ⟶ "1000000000"
│ ├─ hash_pin("1357") ⟶ hash_value
│ ├─ create_user_record() ⟶ INSERT INTO users
│ ├─ record_transaction() ⟶ INSERT INTO transactions
│ ├─ generate_receipt() ⟶ SAVE FILE
│ └─ Display success message
│
├─ main_menu() loops
│ └─ User selects: 1 (Login)
│
├─ login()
│ ├─ Input account: "1000000000"
│ ├─ get_user() ⟶ fetch from DB ✅
│ ├─ Input PIN: "1357"
│ ├─ hash_pin("1357") ⟶ check against DB hash ✅
│ ├─ reset_failed_attempts()
│ └─ Return (account, user) to main_menu
│
├─ atm_menu("1000000000")
│ └─ User selects: 3 (Withdraw)
│
├─ withdraw("1000000000")
│ ├─ get_user() ⟶ fetch current balance (5000.00)
│ ├─ Input amount: "1000"
│ │
│ ├─ Validation 1: Min balance
│ │ 5000 - 1000 = 4000 >= 500 ✅
│ │
│ ├─ Validation 2: Daily limit
│ │ 0 + 1000 <= 20000 ✅
│ │
│ ├─ Validation 3: ATM cash
│ │ 1000000 >= 1000 ✅
│ │
│ ├─ get_db_transaction()
│ │ ├─ UPDATE users: balance 5000 ⟶ 4000
│ │ ├─ UPDATE settings: atm_cash 1000000 ⟶ 999000
│ │ ├─ INSERT transaction: WITHDRAW
│ │ └─ AUTO-COMMIT ✅
│ │
│ ├─ generate_receipt() ⟶ SAVE FILE
│ └─ Display success message
│
├─ atm_menu() continues
│ └─ User selects: 6 (Logout)
│
├─ main_menu() loops
│ └─ User selects: 4 (Exit)
│
└─ Program exits
└─ Thank you message
Conclusion
This project is a beginner-to-intermediate yet robust ATM management system built in Python with SQLite, offering secure multi-user account handling, PIN-based authentication, and a full set of banking operations (login, account creation, balance inquiry, deposit, withdrawal, mini statement, and PIN change) through a simple command-line interface. It stores users and transactions in a structured database, enforces rules like minimum balance, daily withdrawal limits, and account lockout after repeated failures, and even generates masked receipts, making it a practical template for learning real-world banking logic, security practices, and database-backed application design.
Future Enhancements
Potential improvements for production deployment:
- Add unique salt per user for PIN hashing.
- Implement transaction reversal/refund functionality.
- Add multi-factor authentication.
- Create user-specific withdrawal limits.
- Implement transaction search and filtering.
- Add email/SMS notifications for transactions.
- Create web-based interface.
- Add account closure functionality.
- Implement interest calculation on savings.
- Add support for multiple currencies.
- Create detailed audit logs for compliance
This project is designed for educational purposes and demonstrates core banking system concepts including database management, security implementation, and transaction processing.
Default Admin Credentials
- Username: Admin
- Password: SecureAdmin@2025
- Security Warning: Change the default admin password immediately after first login via the Admin Panel ⟶ Change Admin Password option.
Final Remarks
This ATM system is well-structured for a learning project with solid fundamentals:
- ✅ Proper use of SQLite transactions and parameterized queries.
- ✅ Security-conscious (hashing, masking, account lockout).
- ✅ Multi-user support with persistent state.
- ✅ Comprehensive feature set (admin panel, daily limits, mini statements).
Related Sources
Official Documentation
- Python sqlite3 Module
- Python getpass Module
- contextlib – Context Manager Utilities
- PEP 8 – Style Guide for Python Code
- PEP 484 – Type Hints
- PEP 391 – Dictionary-Based Logging Configuration
Security Best Practices
- OWASP Password Storage Cheat Sheet
- OWASP Cryptographic Storage Cheat Sheet
- OWASP SQL Injection Prevention Cheat Sheet
- Auth0 – Password Salting
Database & Transactions
Design Patterns
- Factory Method Pattern – Real Python
- Factory Method – Refactoring Guru
- Python Context Managers Tutorial
Code Quality & Testing
- PEP 8 Guide – Real Python
- Python Logging Best Practices – Last9
- Python Logging Best Practices – Better Stack
SQL Injection Prevention
The code is educational and functional for learning purposes, but would need security hardening and bug fixes before deploying in a real banking environment.
Happy Coding!
C Programming
Tutorial
Complete C Programming Tutorial for Beginners is a step-by-step C language course that teaches core concepts from scratch, starting with setup and Hello World, then moving through variables, operators, input/output, conditions, loops, functions, arrays, strings, pointers, structures, and basic file handling with clear examples and practice exercises.
Go To TutorialOther Projects
Shooter Game
This is a beginner-friendly guide for building a Space Shooter game with Python and Pygame, covering coding concepts and project structure.
View Project →
To-Do CLI App
Interactive command-line to-do list manager with Python, featuring list operations, persistent tasks, and practical coding exercises.
View Project →
Weather App
Responsive weather app with real-time API data, feature comparison, and intuitive design for global city forecasts.
View Project →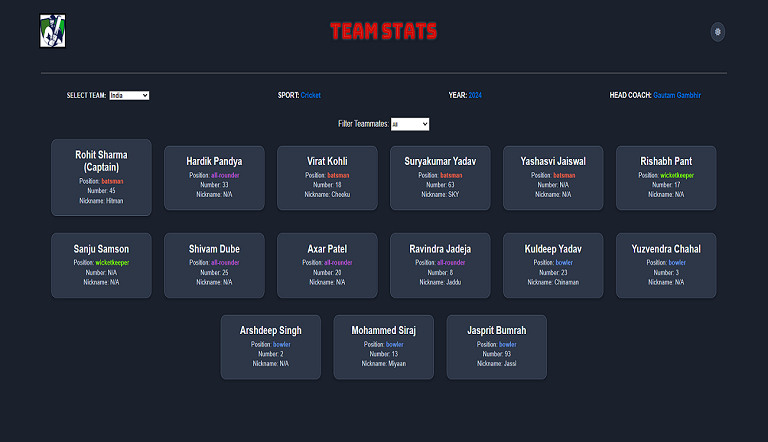
Team Card App
Interactive team card application for cricket, featuring dynamic team selection, player filters, and customizable light/dark themes.
View Project →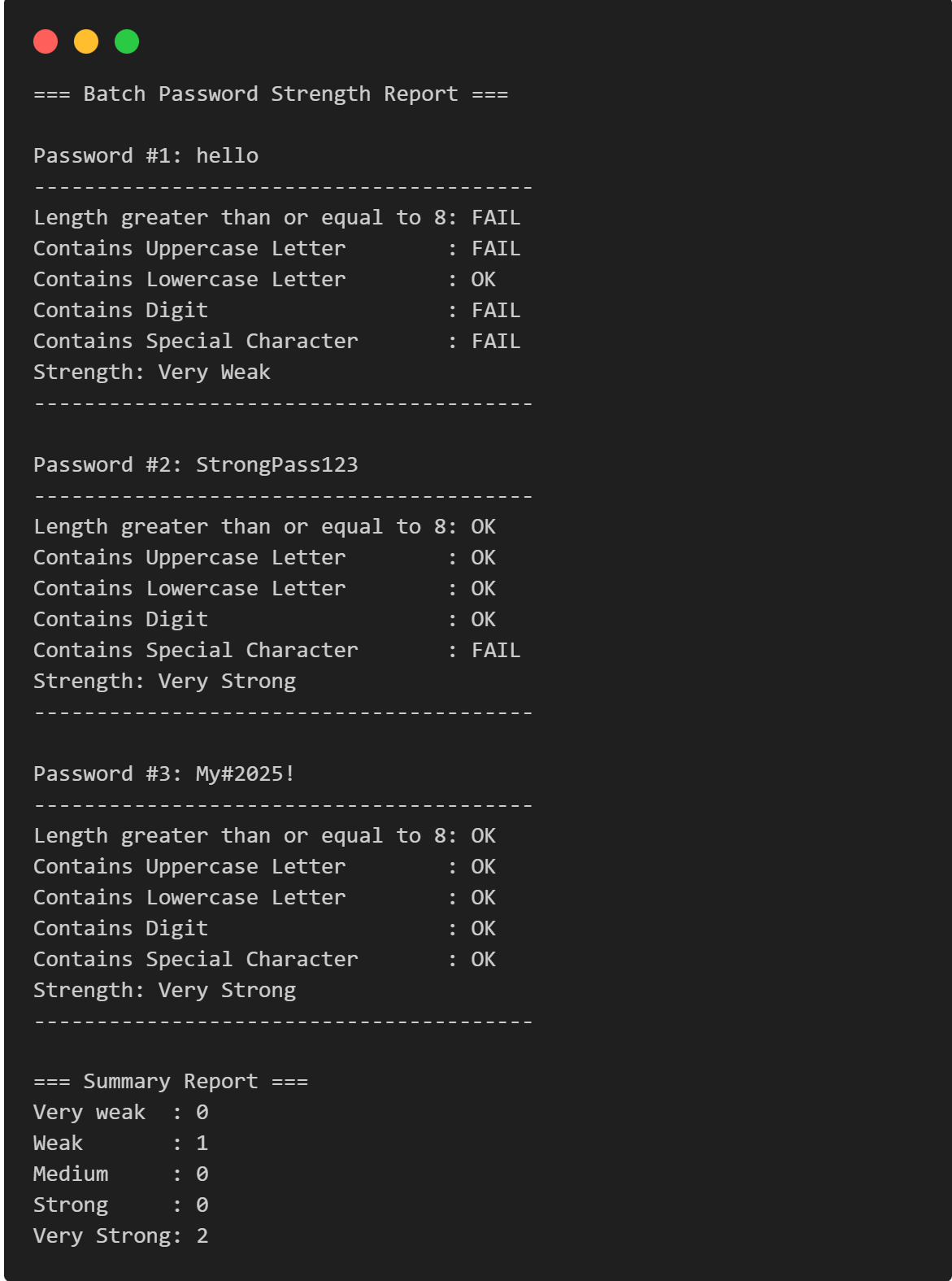
Password Strength Checker
Multi-Password Batch Strength Checker (C++), designed to check multiple passwords at once, show individual strength, and provide a summary report.
View Project →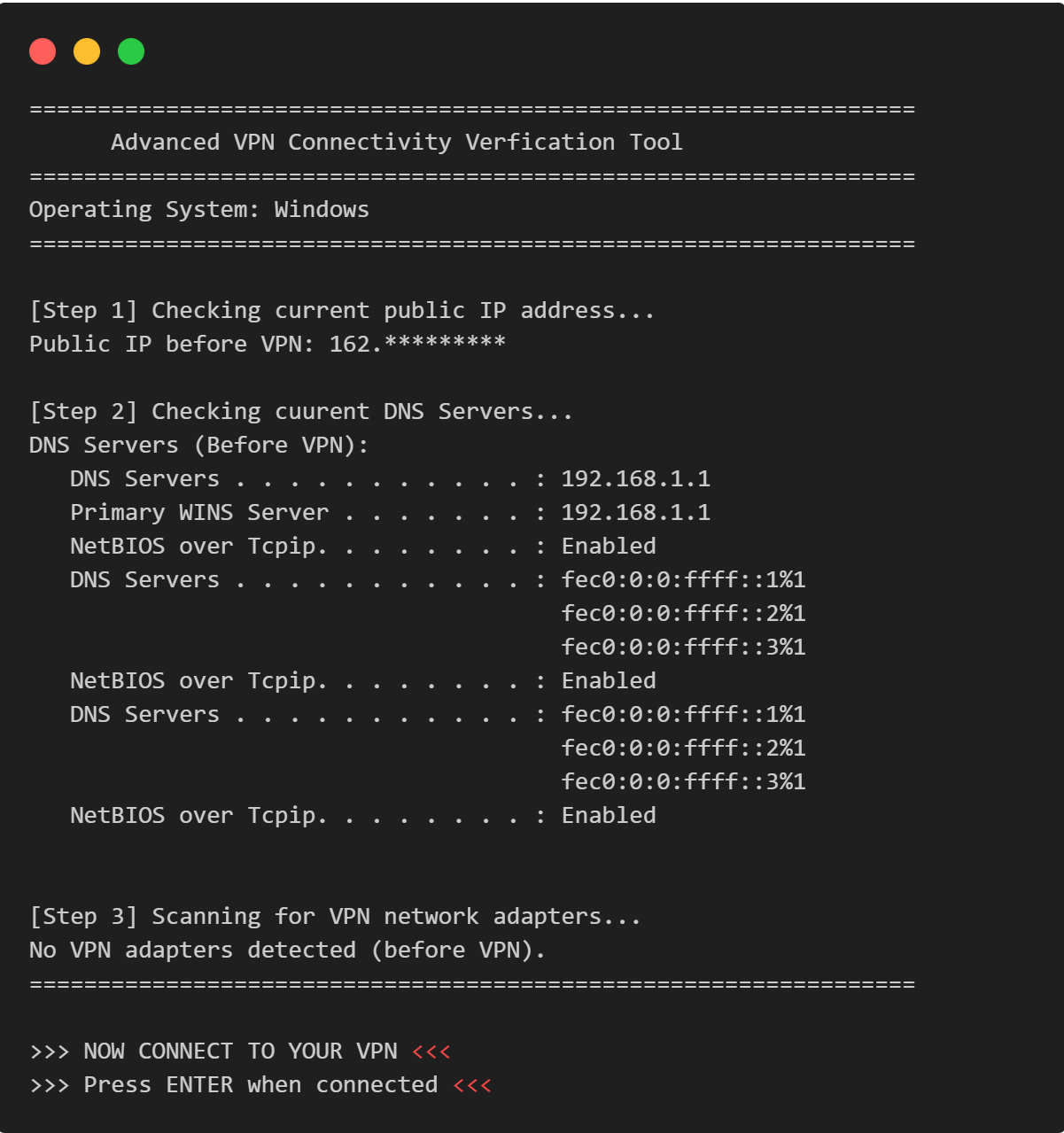
VPN Connectivity verification in C
Efficient C program to verify VPN status, routing, and DNS configurations through comprehensive public IP and network adapter analysis.
View Project →