Simple Calculator in C: Complete Tutorial with CLI Interface
Learn How to Create a Simple Calculator in C: Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners
This comprehensive simple calculator in C tutorial teaches you how to build a fully functional menu-driven calculator with a command-line interface from scratch. Perfect for beginner C programmers, this project demonstrates essential programming concepts including function organization, switch statement control flow, input validation, and error handling. Learn to create a C calculator program that performs five arithmetic operations—addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and modulus—with professional input validation and zero-division protection. This step-by-step guide includes complete source code, compilation instructions, common mistake solutions, and practice exercises to strengthen your C programming foundation.
Table of Contents
Implementation Details
This project is perfect for beginners learning C programming as it covers essential concepts like functions, switch statements, input validation, and user interaction.
What This Project Does
Our calculator will perform five basic mathematical operations:
- ➕ Addition
- ➖ Subtraction
- ✖️ Multiplication
- ➗ Division (with zero-division protection)
- 📊 Modulus (remainder operation)
Why This Project Is Useful
- Practical Application: Demonstrates real-world programming concepts.
- Function Usage: Shows how to organize code with modular functions.
- Input Validation: Teaches error handling and user input validation.
- Menu Systems: Introduces menu-driven programming patterns.
- Foundation Building: Perfect stepping stone to more complex projects.
Program Flow and Logic
Here's how our calculator works step by step:
START
|
┌─────▼─────┐
│ Display │
│ Menu │
└─────┬─────┘
│
┌─────▼─────┐
│ Get │
│User Choice│
└─────┬─────┘
│
┌─────▼─────┐ NO
│Choice = 6?├────────┐
│ (Exit) │ │
└─────┬─────┘ │
│ YES │
┌─────▼─────┐ │
│ END │ │
└───────────┘ │
│
┌─────────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────┐
│ Get Two │
│ Numbers │
└─────┬───────┘
│
┌─────▼─────┐
│ Perform │
│ Operation │
│ (Switch) │
└─────┬─────┘
│
┌─────▼─────┐
│ Display │
│ Result │
└─────┬─────┘
│
┌─────▼─────┐
│Continue or│
│ Exit? │
└─────┬─────┘
│
└──────────────┐
│
┌────▼────┐
│ LOOP │
│ BACK │
└─────────┘
Key Programming Concepts Used:
- Functions: Each operation has its own function.
- Switch Statement: Menu selection handling.
- Do-While Loop: Continues until user exits.
- Input Validation: Prevents errors and crashes.
- Modular Design: Clean, organized code structure
Complete Source Code
Calculator.c
/*
===============================================================================
SIMPLE CALCULATOR - CLI VERSION
===============================================================================
Description: A beginner-friendly calculator program in C with menu interface
Author: C Programming Tutorial
Features: Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication, Division, Modulus
Compilation: gcc -Wall -Wextra -std=c99 -o calculator calculator.c
===============================================================================
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
/* ===============================================================================
FUNCTION PROTOTYPES
=============================================================================== */
// Mathematical operation functions
double add(double a, double b);
double subtract(double a, double b);
double multiply(double a, double b);
double divide(double a, double b);
int modulus(int a, int b);
// Utility functions
void displayMenu(void);
void clearInputBuffer(void);
int getValidChoice(void);
double getValidNumber(const char* prompt);
void displayResult(double result, const char* operation);
void pressEnterToContinue(void);
/* ===============================================================================
MAIN FUNCTION
=============================================================================== */
int main(void) {
int choice;
double num1, num2, result;
printf("\n");
printf("===============================================================================\n");
printf(" WELCOME TO SIMPLE CALCULATOR v1.0\n");
printf("===============================================================================\n");
printf("This calculator performs basic mathematical operations.\n");
printf("Follow the menu prompts to perform calculations.\n");
// Main program loop - continues until user chooses to exit
do {
displayMenu();
choice = getValidChoice();
// Handle exit option
if (choice == 6) {
printf("\n");
printf("===============================================================================\n");
printf(" THANK YOU FOR USING THE CALCULATOR!\n");
printf("===============================================================================\n");
break;
}
// Get input numbers for calculation
printf("\n");
num1 = getValidNumber("Enter first number: ");
num2 = getValidNumber("Enter second number: ");
printf("\n");
printf("===============================================================================\n");
// Perform calculation based on user choice
switch (choice) {
case 1: // Addition
result = add(num1, num2);
displayResult(result, "Addition");
printf("%.2f + %.2f = %.2f\n", num1, num2, result);
break;
case 2: // Subtraction
result = subtract(num1, num2);
displayResult(result, "Subtraction");
printf("%.2f - %.2f = %.2f\n", num1, num2, result);
break;
case 3: // Multiplication
result = multiply(num1, num2);
displayResult(result, "Multiplication");
printf("%.2f × %.2f = %.2f\n", num1, num2, result);
break;
case 4: // Division
if (num2 == 0) {
printf(" ERROR: DIVISION BY ZERO\n");
printf("===============================================================================\n");
printf("❌ Cannot divide by zero! Please try again with a non-zero divisor.\n");
} else {
result = divide(num1, num2);
displayResult(result, "Division");
printf("%.2f ÷ %.2f = %.2f\n", num1, num2, result);
}
break;
case 5: // Modulus
// Modulus only works with integers
if (num2 == 0) {
printf(" ERROR: MODULUS BY ZERO\n");
printf("===============================================================================\n");
printf("❌ Cannot perform modulus by zero! Please try again.\n");
} else {
int intNum1 = (int)num1;
int intNum2 = (int)num2;
int modResult = modulus(intNum1, intNum2);
printf(" MODULUS RESULT\n");
printf("===============================================================================\n");
printf("✓ %d %% %d = %d\n", intNum1, intNum2, modResult);
}
break;
default:
printf(" INVALID CHOICE\n");
printf("===============================================================================\n");
printf("❌ Please select a valid option (1-6).\n");
}
pressEnterToContinue();
} while (choice != 6);
return 0;
}
/* ===============================================================================
MATHEMATICAL OPERATION FUNCTIONS
=============================================================================== */
/**
* Addition function
* @param a: First number
* @param b: Second number
* @return: Sum of a and b
*/
double add(double a, double b) {
return a + b;
}
/**
* Subtraction function
* @param a: First number (minuend)
* @param b: Second number (subtrahend)
* @return: Difference of a and b
*/
double subtract(double a, double b) {
return a - b;
}
/**
* Multiplication function
* @param a: First number
* @param b: Second number
* @return: Product of a and b
*/
double multiply(double a, double b) {
return a * b;
}
/**
* Division function
* @param a: Dividend
* @param b: Divisor (should not be zero)
* @return: Quotient of a divided by b
*/
double divide(double a, double b) {
return a / b;
}
/**
* Modulus function (remainder after division)
* @param a: Dividend (integer)
* @param b: Divisor (integer, should not be zero)
* @return: Remainder of a divided by b
*/
int modulus(int a, int b) {
return a % b;
}
/* ===============================================================================
UTILITY FUNCTIONS
=============================================================================== */
/**
* Display the main menu options
*/
void displayMenu(void) {
printf("\n");
printf("===============================================================================\n");
printf(" CALCULATOR MENU\n");
printf("===============================================================================\n");
printf("Choose an operation:\n");
printf(" 1. ➕ Addition (a + b)\n");
printf(" 2. ➖ Subtraction (a - b)\n");
printf(" 3. ✖️ Multiplication (a × b)\n");
printf(" 4. ➗ Division (a ÷ b)\n");
printf(" 5. 📊 Modulus (a %% b)\n");
printf(" 6. 🚪 Exit Program\n");
printf("===============================================================================\n");
}
/**
* Clear input buffer to handle invalid input
*/
void clearInputBuffer(void) {
int c;
while ((c = getchar()) != '\n' && c != EOF) {
// Clear the input buffer
}
}
/**
* Get valid menu choice from user
* @return: Valid choice (1-6)
*/
int getValidChoice(void) {
int choice;
while (1) {
printf("Enter your choice (1-6): ");
if (scanf("%d", &choice) == 1) {
clearInputBuffer();
if (choice >= 1 && choice <= 6) {
return choice;
} else {
printf("❌ Invalid choice! Please enter a number between 1 and 6.\n\n");
}
} else {
clearInputBuffer();
printf("❌ Invalid input! Please enter a numeric choice (1-6).\n\n");
}
}
}
/**
* Get valid number from user with custom prompt
* @param prompt: Message to display to user
* @return: Valid floating-point number
*/
double getValidNumber(const char* prompt) {
double number;
while (1) {
printf("%s", prompt);
if (scanf("%lf", &number) == 1) {
clearInputBuffer();
return number;
} else {
clearInputBuffer();
printf("❌ Invalid input! Please enter a valid number.\n");
}
}
}
/**
* Display formatted result header
* @param result: The calculated result
* @param operation: Name of the operation performed
*/
void displayResult(double result, const char* operation) {
printf(" %s RESULT\n", operation);
printf("===============================================================================\n");
printf("✓ ");
}
/**
* Pause program and wait for user to press Enter
*/
void pressEnterToContinue(void) {
printf("\n📝 Press Enter to continue...");
getchar();
}
/* ===============================================================================
END OF PROGRAM
=============================================================================== */
Compilation and Execution
gcc -Wall -Wextra -std=c99 -o calculator calculator.c
How to Run:
./calculator # Linux/Mac
calculator.exe # Windows
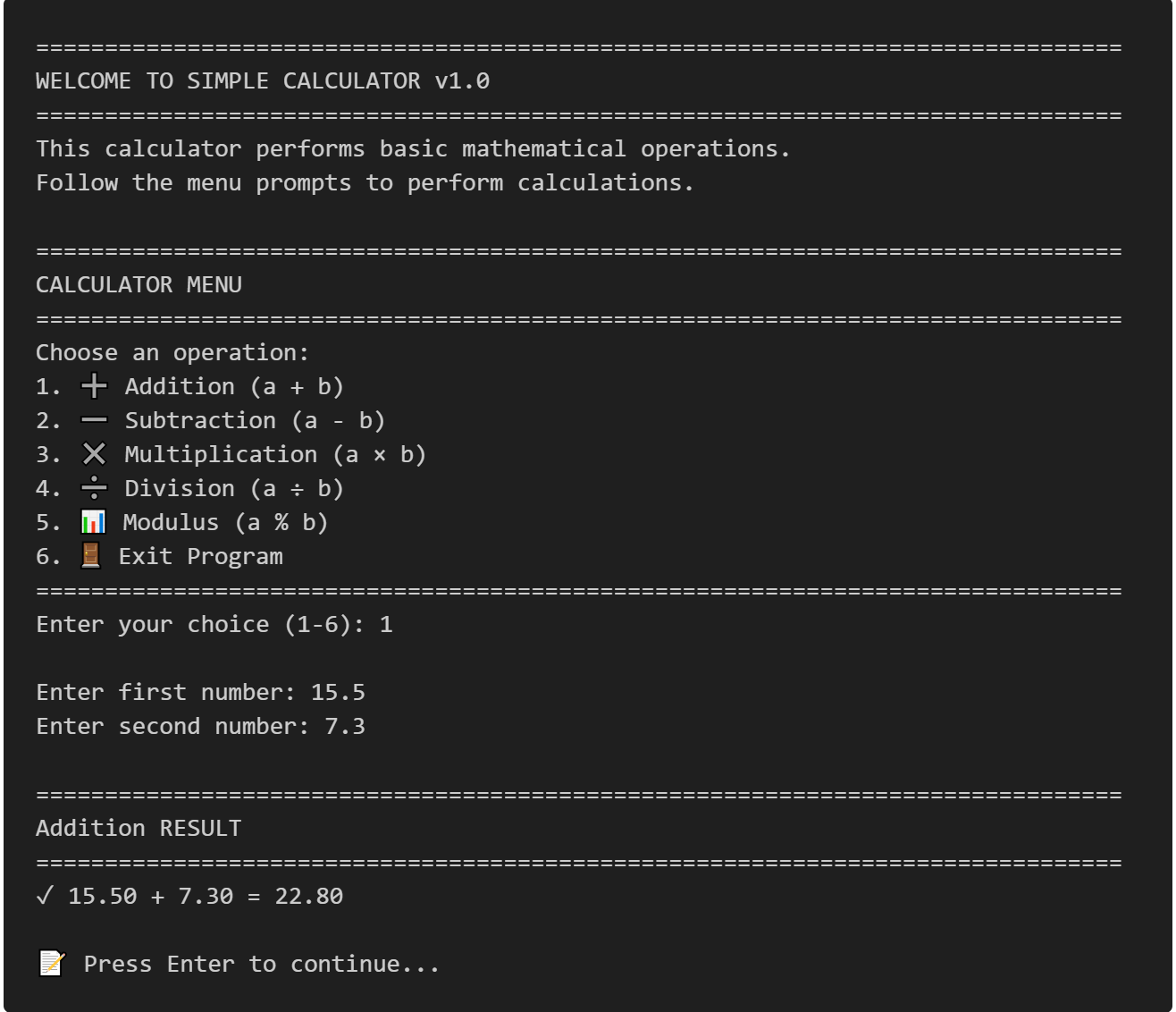
Sample Input and Output
Here's what you'll see when running the program:
===============================================================================
WELCOME TO SIMPLE CALCULATOR v1.0
===============================================================================
This calculator performs basic mathematical operations.
Follow the menu prompts to perform calculations.
===============================================================================
CALCULATOR MENU
===============================================================================
Choose an operation:
1. ➕ Addition (a + b)
2. ➖ Subtraction (a - b)
3. ✖️ Multiplication (a × b)
4. ➗ Division (a ÷ b)
5. 📊 Modulus (a % b)
6. 🚪 Exit Program
===============================================================================
Enter your choice (1-6): 1
Enter first number: 15.5
Enter second number: 7.3
===============================================================================
Addition RESULT
===============================================================================
✓ 15.50 + 7.30 = 22.80
📝 Press Enter to continue...
===============================================================================
CALCULATOR MENU
===============================================================================
Choose an operation:
1. ➕ Addition (a + b)
2. ➖ Subtraction (a - b)
3. ✖️ Multiplication (a × b)
4. ➗ Division (a ÷ b)
5. 📊 Modulus (a % b)
6. 🚪 Exit Program
===============================================================================
Enter your choice (1-6): 4
Enter first number: 100
Enter second number: 0
===============================================================================
ERROR: DIVISION BY ZERO
===============================================================================
❌ Cannot divide by zero! Please try again with a non-zero divisor.
📝 Press Enter to continue...
Common Mistakes and Debugging Tips
1. Forgetting break in Switch Statements
❌ Wrong:
switch (choice) {
case 1:
result = add(num1, num2);
// Missing break - will continue to case 2!
case 2:
result = subtract(num1, num2);
break;
}
✅ Correct:
switch (choice) {
case 1:
result = add(num1, num2);
break; // Essential!
case 2:
result = subtract(num1, num2);
break;
}
2. Not Handling Division by Zero
❌ Wrong:
double divide(double a, double b) {
return a / b; // Will cause runtime error if b = 0
}
✅ Correct:
// In main function:
if (num2 == 0) {
printf("Error: Cannot divide by zero!\n");
} else {
result = divide(num1, num2);
printf("%.2f ÷ %.2f = %.2f\n", num1, num2, result);
}
3. Input Buffer Problems
❌ Problem: When scanf
fails, invalid input stays
in buffer
scanf("%d", &choice); // If user enters "abc", it stays in buffer
✅ Solution: Clear the buffer after each input
if (scanf("%d", &choice) == 1) {
clearInputBuffer(); // Clear any remaining input
// Process valid input
} else {
clearInputBuffer(); // Clear invalid input
// Handle error
}
4. Infinite Loops in Input Validation
❌ Wrong:
do {
printf("Enter choice: ");
scanf("%d", &choice);
} while (choice < 1 || choice > 6); // No handling of invalid input
✅ Correct:
while (1) {
printf("Enter choice: ");
if (scanf("%d", &choice) == 1 && choice >= 1 && choice <= 6) {
clearInputBuffer();
break; // Valid input received
} else {
clearInputBuffer();
printf("Invalid input! Try again.\n");
}
}
Practice Exercises
Exercise 1: Add Power Operation
Challenge: Add a power operation (a^b) to the calculator.
- Add option 7 to the menu.
- Create a
power()function. - Add a new case in the switch statement.
- You can use a loop or include
<math.h>and usepow()function.
// Add this include at the top
#include
// Add this function
double power(double base, double exponent) {
return pow(base, exponent);
}
// Update the menu display
void displayMenu(void) {
printf("\n");
printf("===============================================================================\n");
printf(" CALCULATOR MENU\n");
printf("===============================================================================\n");
printf("Choose an operation:\n");
printf(" 1. ➕ Addition (a + b)\n");
printf(" 2. ➖ Subtraction (a - b)\n");
printf(" 3. ✖️ Multiplication (a × b)\n");
printf(" 4. ➗ Division (a ÷ b)\n");
printf(" 5. 📊 Modulus (a %% b)\n");
printf(" 6. ⚡ Power (a ^ b)\n"); // New option
printf(" 7. 🚪 Exit Program\n"); // Updated exit option
printf("===============================================================================\n");
}
// Add this case in the switch statement (before case 7)
case 6: // Power
result = power(num1, num2);
displayResult(result, "Power");
printf("%.2f ^ %.2f = %.2f\n", num1, num2, result);
break;
// Update exit condition and validation to use 7 instead of 6
Exercise 2: Add Square Root Operation
Challenge: Add square root functionality that works on a single number.
- Add square root option to menu.
- Only ask for one number (not two).
- Validate that the number is non-negative.
- Use
sqrt()from<math.h>function.
// Add this function
double squareRoot(double number) {
return sqrt(number);
}
// Add to menu (option 7, making exit option 8)
printf(" 7. √ Square Root (√a)\n");
printf(" 8. 🚪 Exit Program\n");
// Add this case in switch statement
case 7: // Square Root
if (num1 < 0) {
printf(" ERROR: NEGATIVE NUMBER\n");
printf("===============================================================================\n");
printf("❌ Cannot calculate square root of negative number!\n");
} else {
result = squareRoot(num1);
displayResult(result, "Square Root");
printf("√%.2f = %.2f\n", num1, result);
}
break;
// Note: For square root, you might want to modify the input logic
// to only ask for one number when choice == 7
Exercise 2: Add Memory Functions
Challenge: Implement basic memory functions (M+, M-, MR, MC) like a real calculator.
- Add global memory variable.
- Add menu options for Memory Add, Memory Subtract, Memory Recall, Memory Clear.
- Allow using memory value as input for calculationse.
// Add global variable
double memory = 0.0;
// Add these functions
void memoryAdd(double value) {
memory += value;
printf("✓ Memory: %.2f (Added %.2f)\n", memory, value);
}
void memorySubtract(double value) {
memory -= value;
printf("✓ Memory: %.2f (Subtracted %.2f)\n", memory, value);
}
void memoryRecall(void) {
printf("✓ Memory Recall: %.2f\n", memory);
}
void memoryClear(void) {
memory = 0.0;
printf("✓ Memory Cleared\n");
}
// Update menu with memory options (9-12)
printf(" 9. M+ Memory Add\n");
printf(" 10. M- Memory Subtract\n");
printf(" 11. MR Memory Recall\n");
printf(" 12. MC Memory Clear\n");
printf(" 13. 🚪 Exit Program\n");
// Add cases in switch statement
case 9: // Memory Add
num1 = getValidNumber("Enter number to add to memory: ");
memoryAdd(num1);
break;
case 10: // Memory Subtract
num1 = getValidNumber("Enter number to subtract from memory: ");
memorySubtract(num1);
break;
case 11: // Memory Recall
memoryRecall();
break;
case 12: // Memory Clear
memoryClear();
break;
Conclusion
Congratulations! 🎉 You've successfully created a fully functional calculator in C with:
The simple calculator tutorial in C provides an excellent introduction to using basic programming concepts such as variables, user input, conditional statements (if-else or switch-case), and arithmetic operations. By building this project step-by-step, beginners learn how to structure a console application that performs addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division based on user input. This foundational exercise helps new programmers develop their logic and C coding skills while gaining confidence in building interactive command-line tools.
Next Steps:
- Try the exercises above to enhance your calculator.
- Add more operations like factorial, trigonometric functions.
- Create a GUI version using libraries like GTK or ncurses.
- Implement expression parsing to evaluate complex expressions like "2+3*4".
- Add history functionality to remember previous calculations.
Key Programming Skills Learned:
- Function definition and organization.
- Switch statement control flow.
- Input validation techniques.
- Error handling patterns.
- User interface design in CLI.
- Modular programming principles.
Keep practicing and building more projects to strengthen your C programming foundation! 🚀
Happy Coding!
Other Projects
Shooter Game
This is a beginner-friendly guide for building a Space Shooter game with Python and Pygame, covering coding concepts and project structure.
View Project →
To-Do CLI App
Interactive command-line to-do list manager with Python, featuring list operations, persistent tasks, and practical coding exercises.
View Project →
Weather App
Responsive weather app with real-time API data, feature comparison, and intuitive design for global city forecasts.
View Project →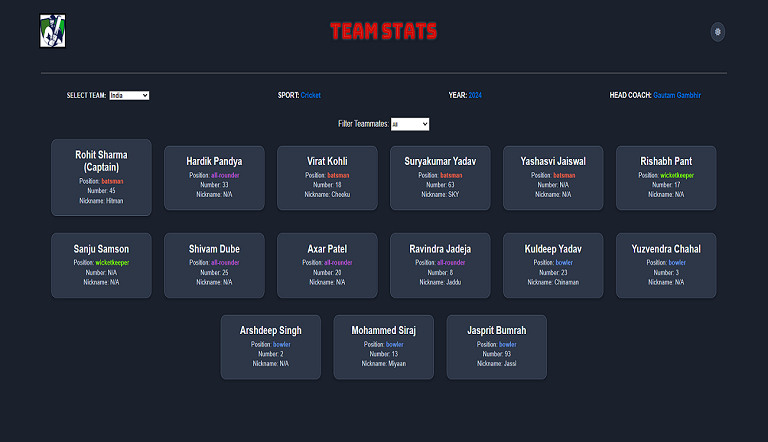
Team Card App
Interactive team card application for cricket, featuring dynamic team selection, player filters, and customizable light/dark themes.
View Project →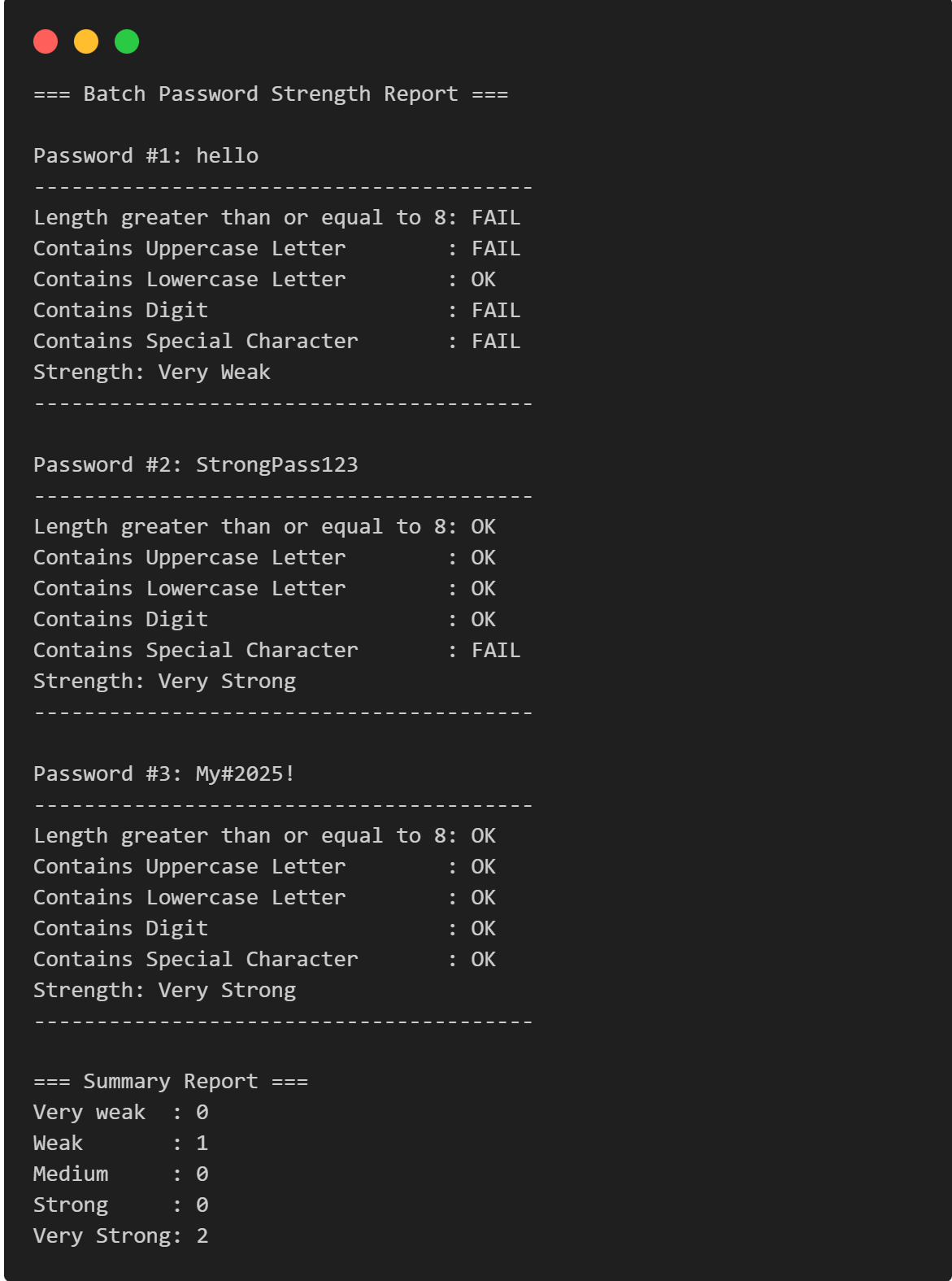
Password Strength Checker
Multi-Password Batch Strength Checker (C++), designed to check multiple passwords at once, show individual strength, and provide a summary report.
View Project →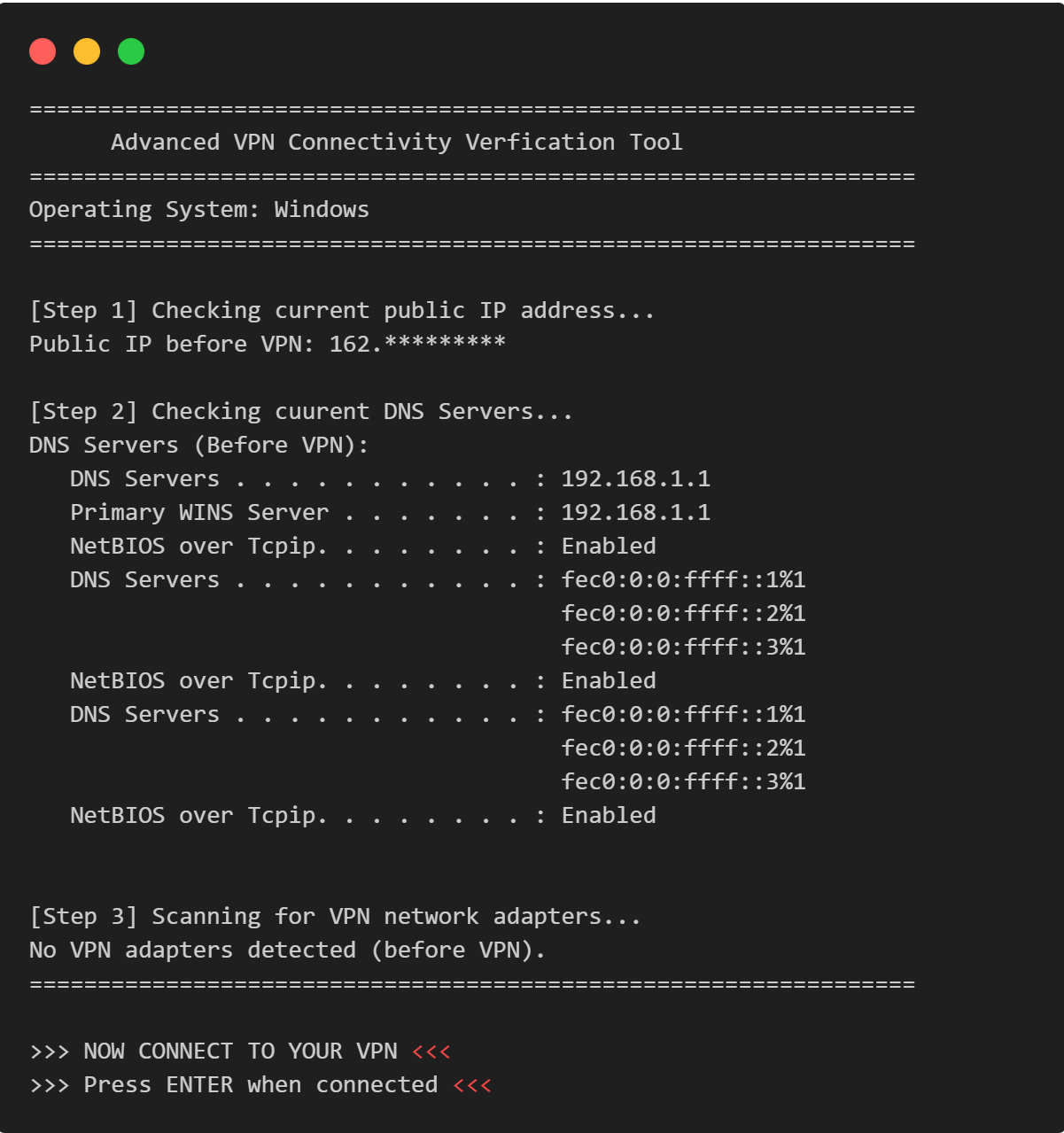
VPN Connectivity verification in C
Efficient C program to verify VPN status, routing, and DNS configurations through comprehensive public IP and network adapter analysis.
View Project →